Spatial Prefetcher
AMPM (access map pattern matching)
https://jilp.org/vol13/v13paper3.pdf
总体上AMPM是一个检测所有可能stride的stride prefetcher
AMPM认为以前的prefetcher有几个关键问题(09年的时候)
- prefetcher只能检测比较简单的pattern, 所以coverage很低
- 在CPU使用了比较大的优化时,比如out-of-order execution, memory访问被打乱,prefetcher无法应对这种乱序
AMPM能够比较好的处理这些问题
- AMPM有比较好的coverage, 他其实相当于一个检测所有stride的stride prefetcher
- AMPM是和memory访问顺序无关的。他主要是观察在每个zone里面的访问模式
a. Main Com ponents
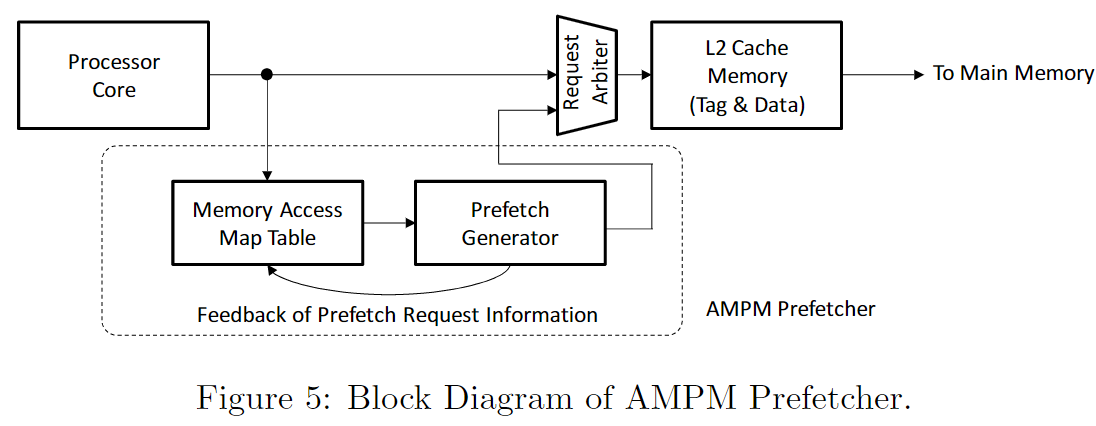
a.i a memory access map
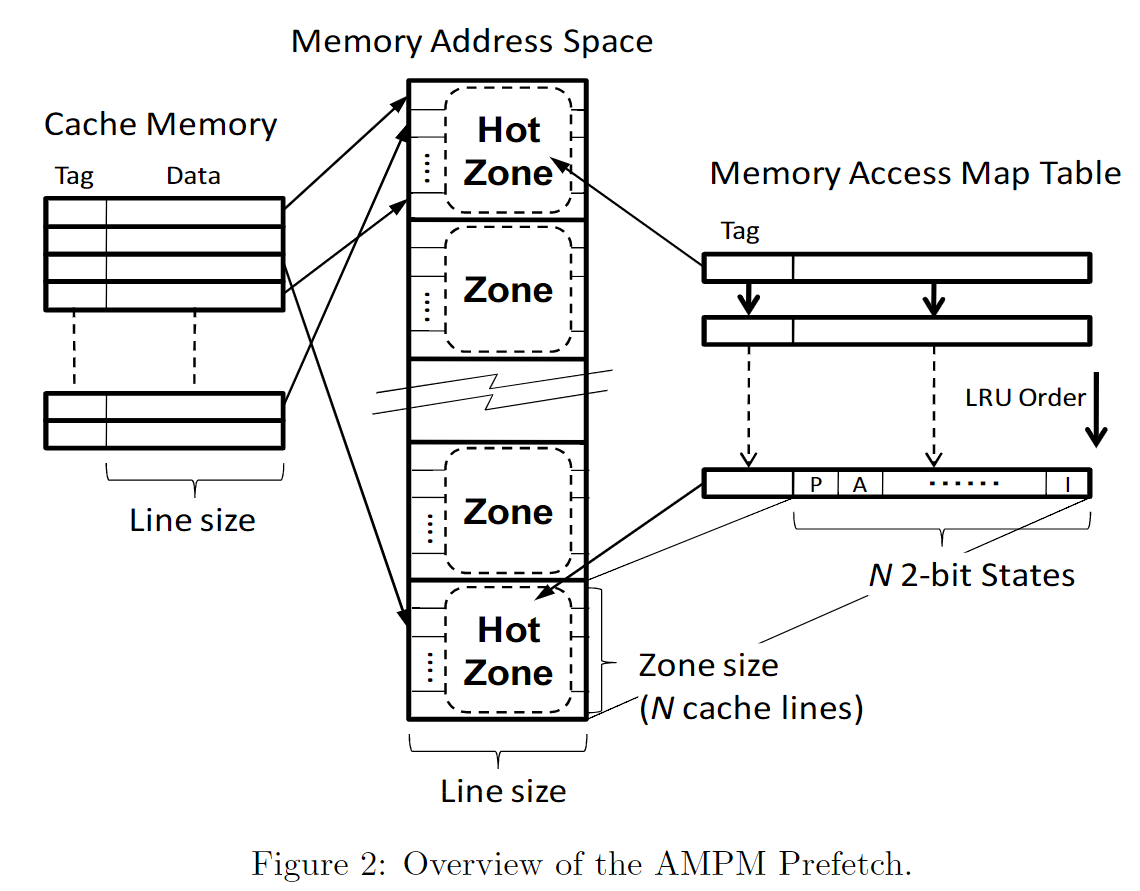
memory access map是一个bitmap的形式,但是其中的每个field都是一个状态机(访问与否,prefetch与否)。
AMPM将Memory划分成一个一个的zone, 比如2KB划分一个zone。
zone可以对应一个memory access map entry。zone中的每个cache line会对应到memory access map中的一个位置,对应该位置的一个状态机。
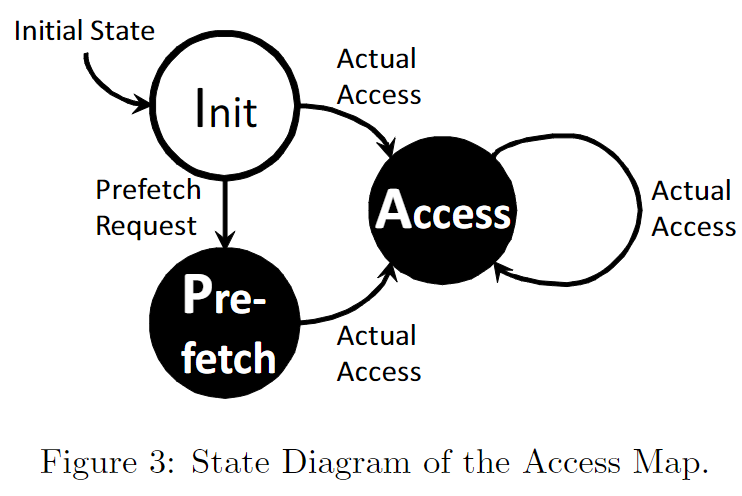
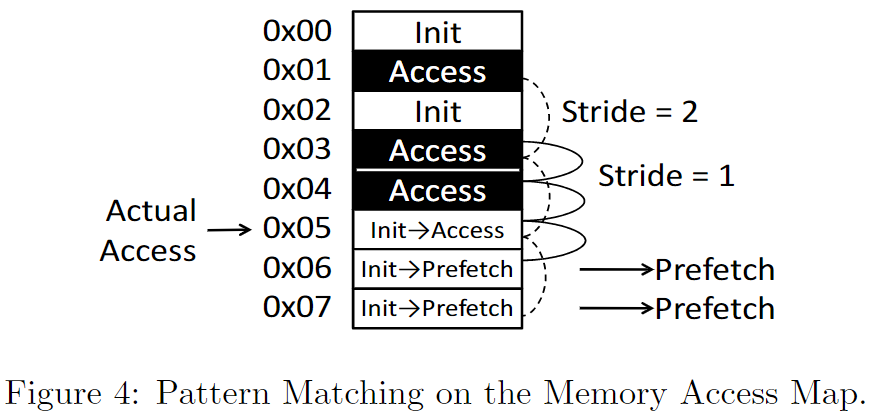
其中状态机的状态转换如下图所示
a.ii hardware pattern matching logic
这个过程中,3个连续的zone的memory access map entry会被读入(前一个zone, 当前zone, 后一个zone),构成一个更大的memory access map。在这个map上,pattern matching logic遍历stride, 生成一些可能的prefetch requests。
stride match的逻辑如下:
t: request addr
N: the number of cache lines in one zone
k: stride
hardware pattern matching logic同时检测memory access map中t+k, t+2k, t+2k+1的状态(k=0,1...N/2-1)。
如果t+k,t+2k(或者t+2k+1)处于Access state, 那么-k是一个可能的stride, t-k会成为一个prefetch candidate
如下是一个例子
0x1, 0x3, 0x4已经被访问了
当前0x5被访问
prefetch generator生成两个candidates
- 0x7 (模式为0x1, 0x3, 0x5)
- 0x6 (模式为0x3, 0x4, 0x5)
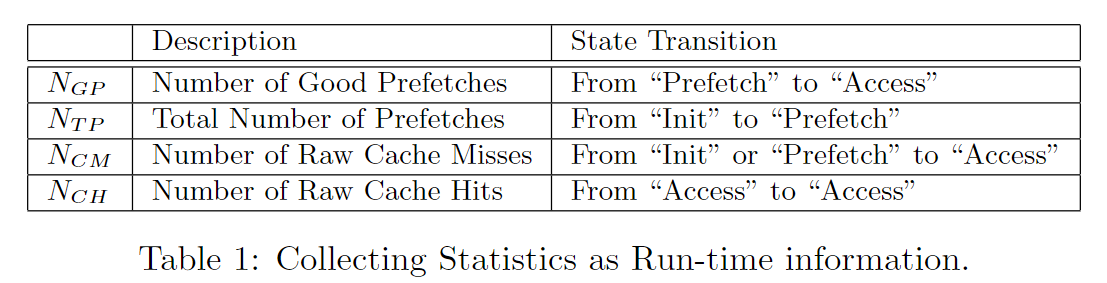
b. Prefetch Degree Control调节逻辑
AMPM在工作过程中会动态调节prefetch degree
BOP
https://hal.inria.fr/hal-01254863/file/BOP_HPCA_2016.pdf
SMS
主要思想:track一个region上的访问模式,形成一个bit pattern。SMS认为如果PC和trigger offset一样的话,访问其他的region也应该是类似的bit-pattern。(Trigger offset是在这个region上第一次访问时的offset)
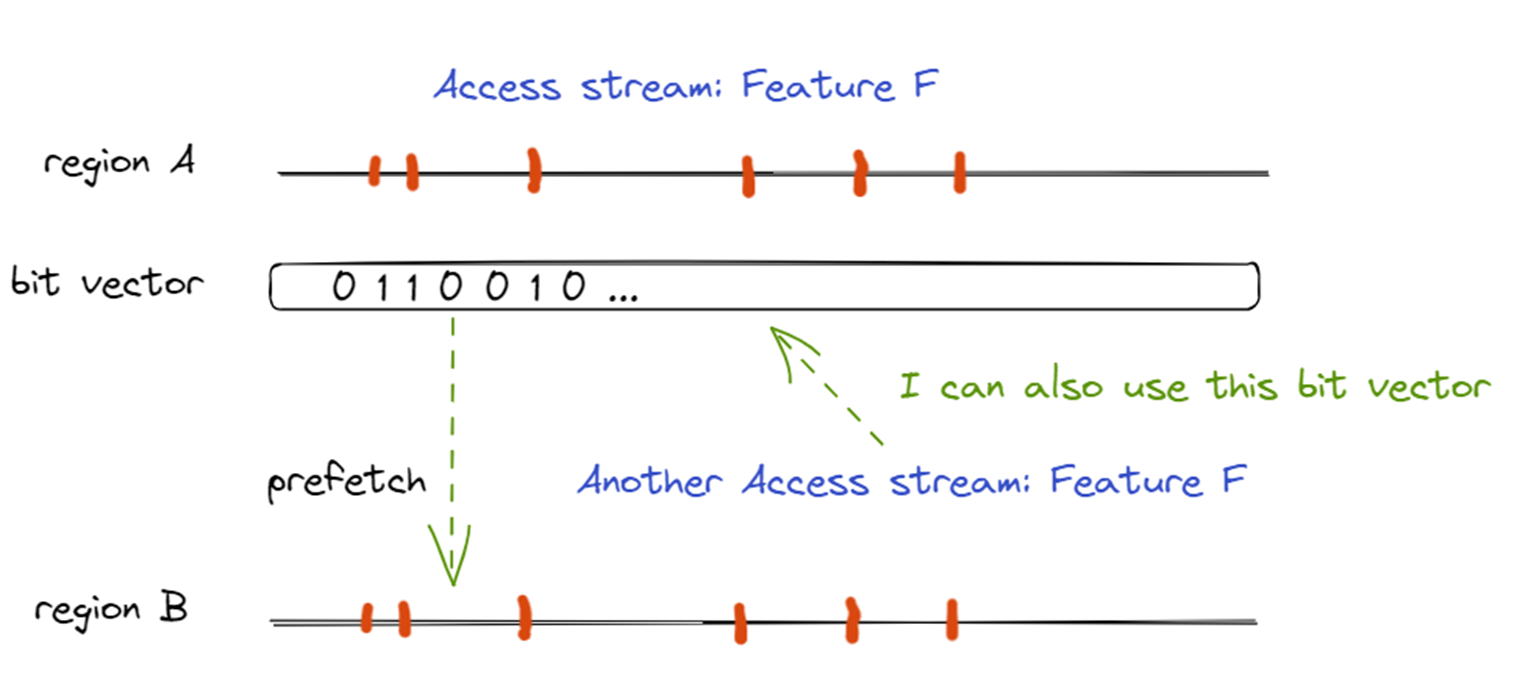
SMS最主要的结构有Accumulation Table, 记录region的bit-pattern。这个pattern训练成熟,也就是被evict的时候,会放入Pattern History Table。
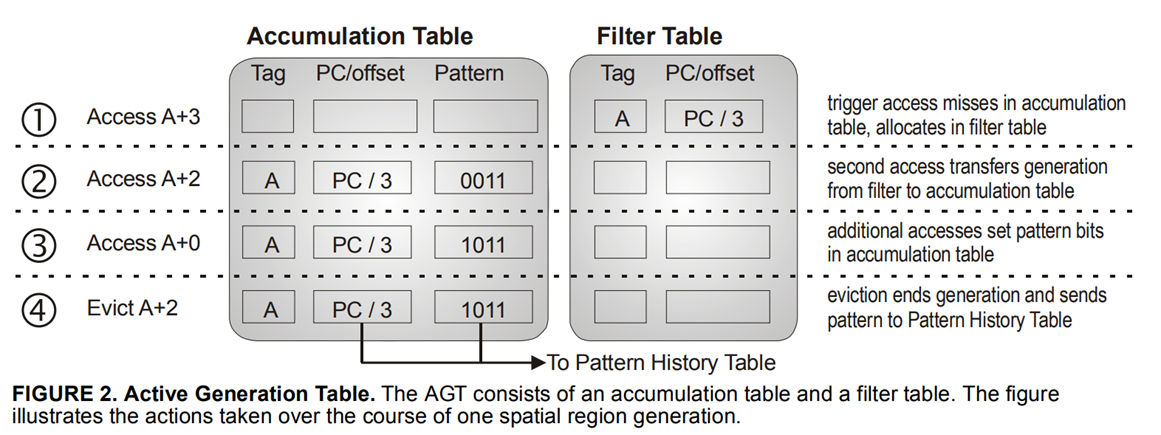
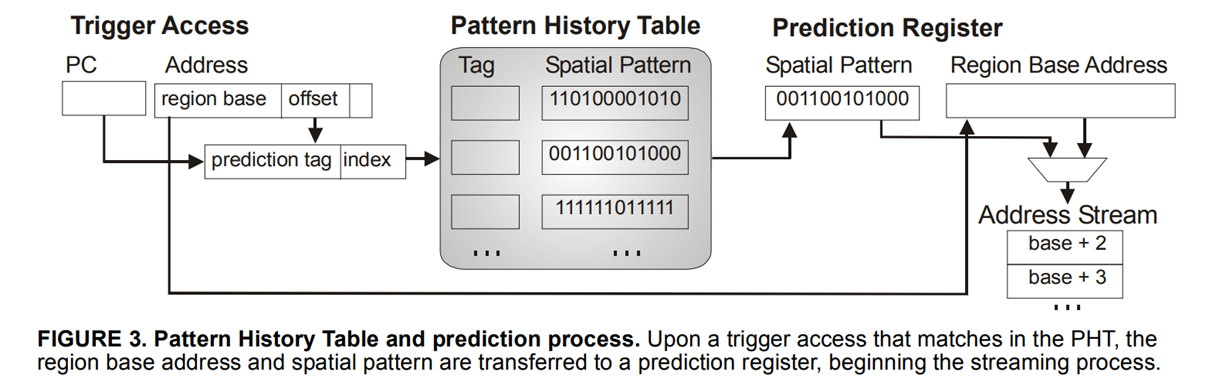
Pattern History Table使用PC+offset索引,然后看bit-pattern中哪些位置1了,就进行prefetch
i. PMP
SMS用了PC+trigger offset作为匹配bit pattern的一个特征
其实还可以选择其他特征,比如用单独pc去匹配,单独用trigger offset, 或者用memory address等等
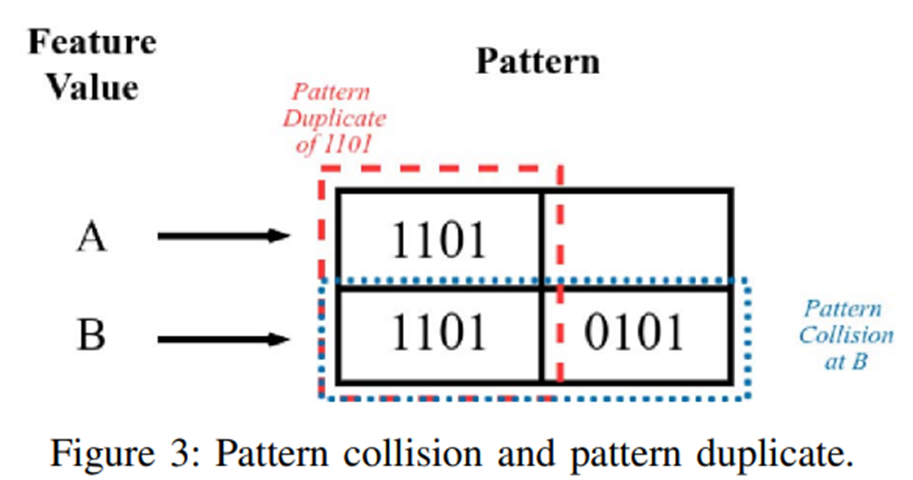
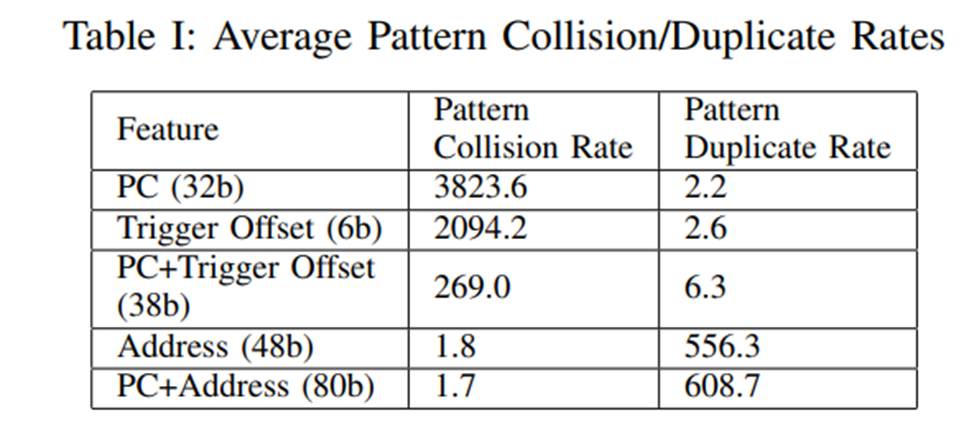
PMP论文中提出了评估这些feature好坏的两个指标,一个是Pattern collision rate, 一个是pattern duplicate rate
- Pattern collision rate是说同一个feature,可能会有很多不同的bit pattern,导致pattern table的bit pattern老是被替换
- Pattern duplicate rate是在一个feature在不同取值情况下,bit pattern是否出现重复,PDR这个越大代表存储的冗余越多
PMP选择了冗余比较少的trigger offset作为一个匹配的feature。同时为了减少trigger offset高PCR的影响,提出了一种merge的方法,比如一个trigger offset对应了几个不同的bit pattern。PMP不是不断的去替换成最新的bit pattern而是将他们merge起来成为一个新的Pattern
a. PMP整体框架
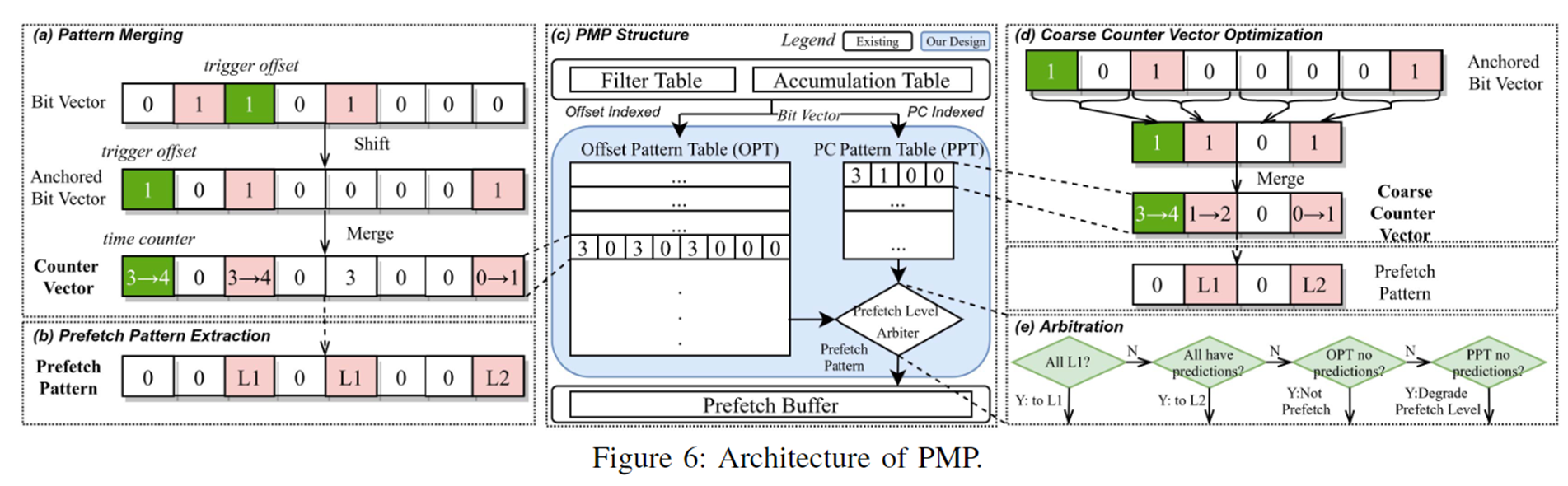
图左边展示了pattern的merge过程。Offset的某个取值如果新来了一个bit pattern, 先根据trigger offset进行一次anchor, 然后和之前的bit pattern相加。
在prefetch的时候,如果counter大于某一置信程度,就会在L1预取,置信程度一般般的话发给让L2预取
在trigger offset这个特征的基础上,PMP还加入了一个辅助特征PC, 他会对预取level的决策产生一些影响
SPP (Signature Path Prefethcer)
进行了一系列内存访问之后,接下来我可能访问哪些数据。
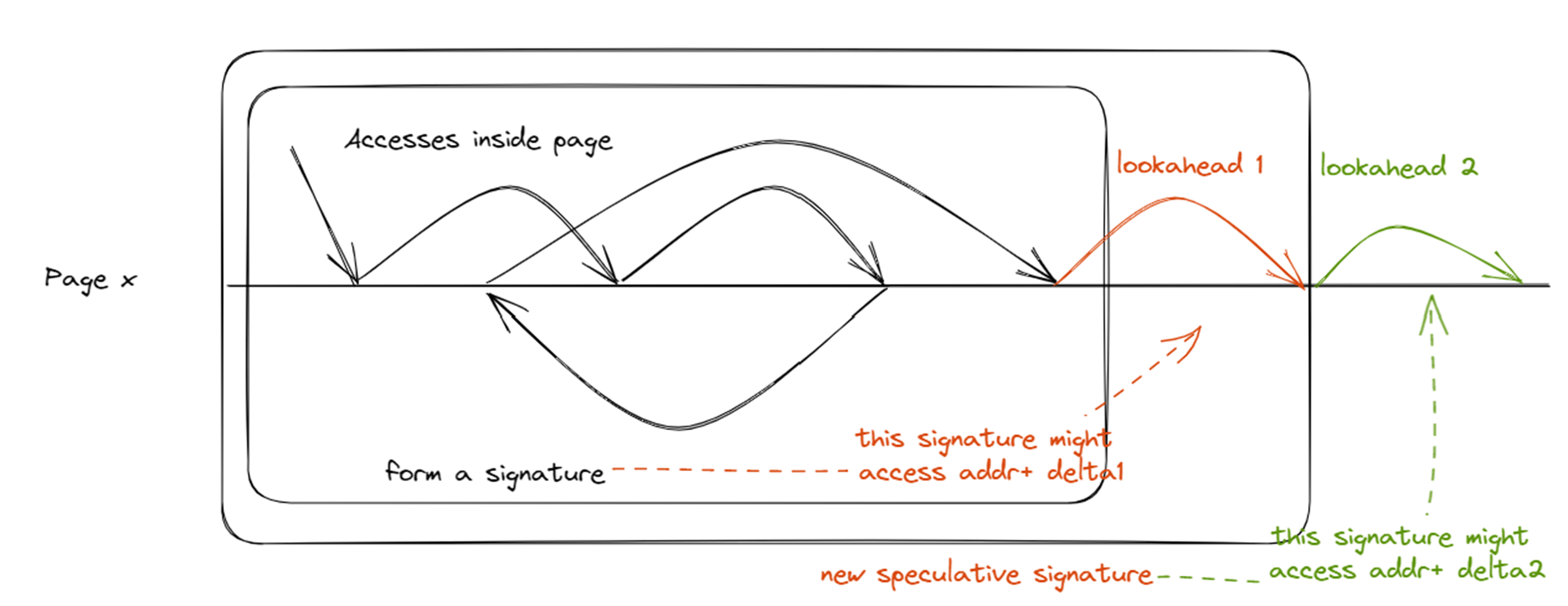
这个一系列内存访问被压缩成一个signature,一个signature会对应几条可能路径(接下来有多大可能性访问A,有多大可能性访问B...)
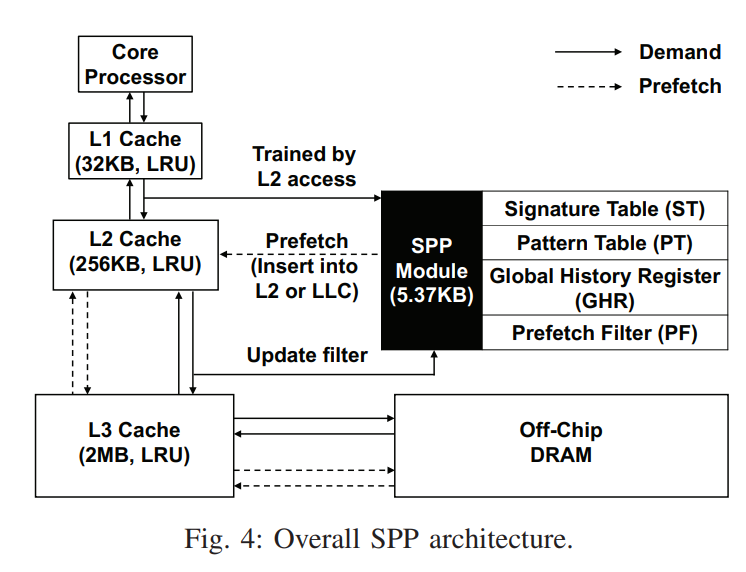
Components
- Signature Table: to capture memory access patterns within 4KB physical pages and to compress the previous deltas in that page into a 12-bit history signature
- Pattern Table
- Prefetch Filter
- Global History Register: cross-page boundary bootstrapped learning
Process
1. Learning Memory Access Patterns
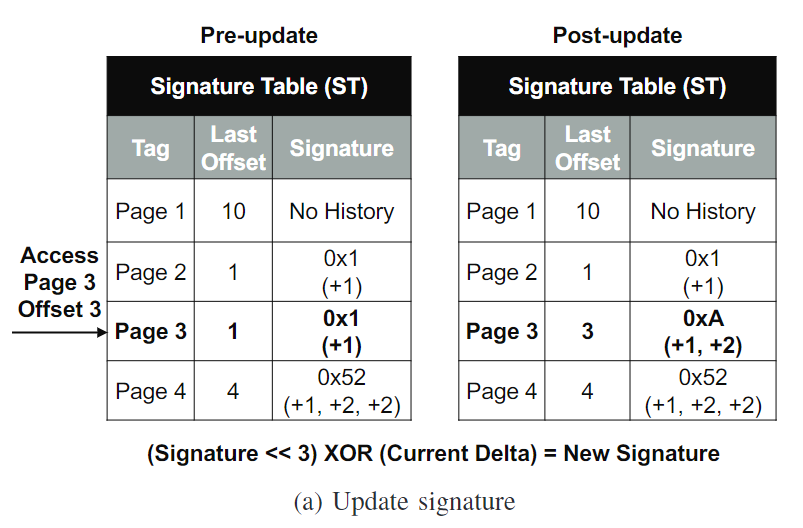
ST存的是什么
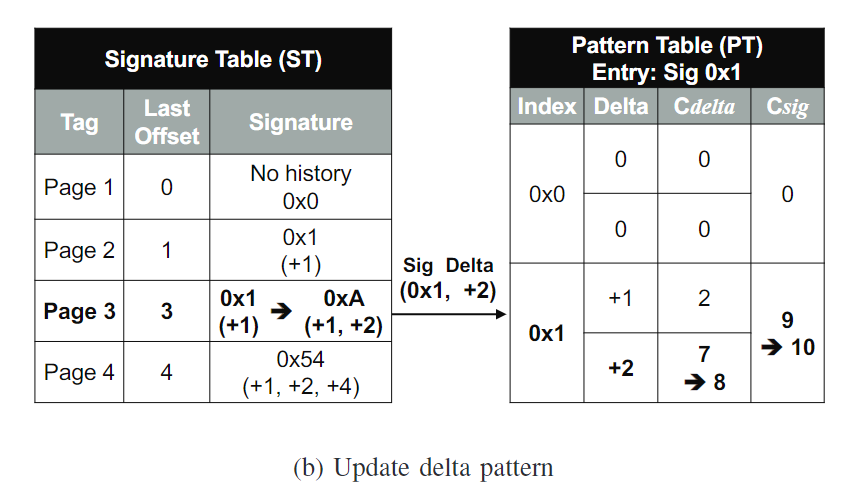
ST里面存了256个最近访问的page, 每个page对应一个最后访问的相对于这个page起始地址的offset(存这个是为了计算delta), 以及一个delta signature。这个delta signature是为了访问和更新PT的
PT存的是什么
PT里面存的是signature,每个signature里面放了几个delta,并给出一个counter来统计可能性,每个signature也会存一个counter用来替换
流程
- 访问ST。L2 cache access来了之后,physical addr传入ST, page number为3, page offset为3。根据他的page number找到对应的entry。可以读到signature是0x1。
- 访问以及更新PT。计算delta = 3 - 1 = 2, 可以推断一系列访问使得signature为1后,会有一个delta为2的访问。由这个signature和delta访问PT,给他们增加置信度,也就是counter的值。如果发生了miss可以做replacement
- 更新ST。根据新的delta (+2)来更新signature。
2. Path Confidence-based Prefetching
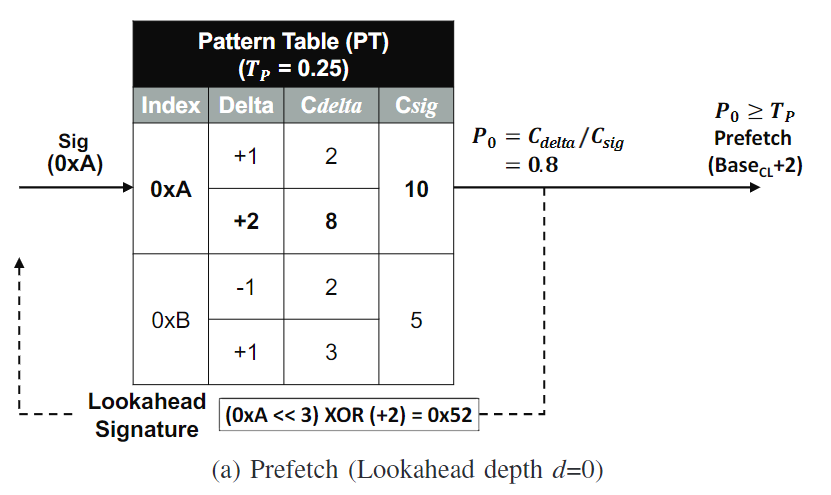
- 更新ST后,得到新的signature A, 访问PT。path confidence为
,这里P0为0.8 - 判断path confidence是否大于某个threshold。如果大于
- PT将当前访问的cache line的base addr加上delta去issue prefetch requests
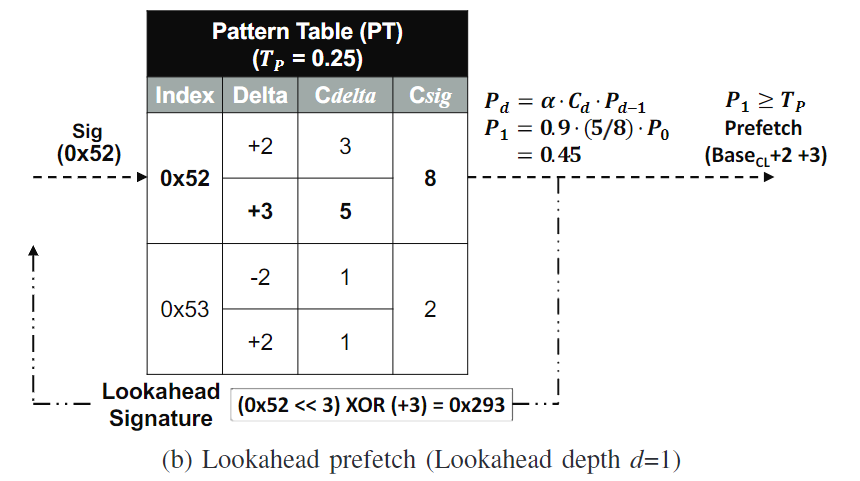
- lookahead。PT用当前的signature以及delta计算得到一个speculative lookahead signature,这里是0x52。然后用这个signature去访问PT,选择confidence最高的delta去prefetch。
- 循环循环。如果confidence低于threshold了就停止。注意confidence是要和前面的相乘的
SPP使用了一个global accuracy scaling factor
Path confidence的计算公式为
如果prefetch accuracy比较高,那么
在两种情况下,SPP会停止prefetch
- Low path confidence
- Too few L2 read queue resources
3. Page Boundary Learning
增加一个记录global history的结构:Global History Register
当SPP做了一个超出page end的prediction, GHR会被更新;当访问一个新的page, GHR会被查询
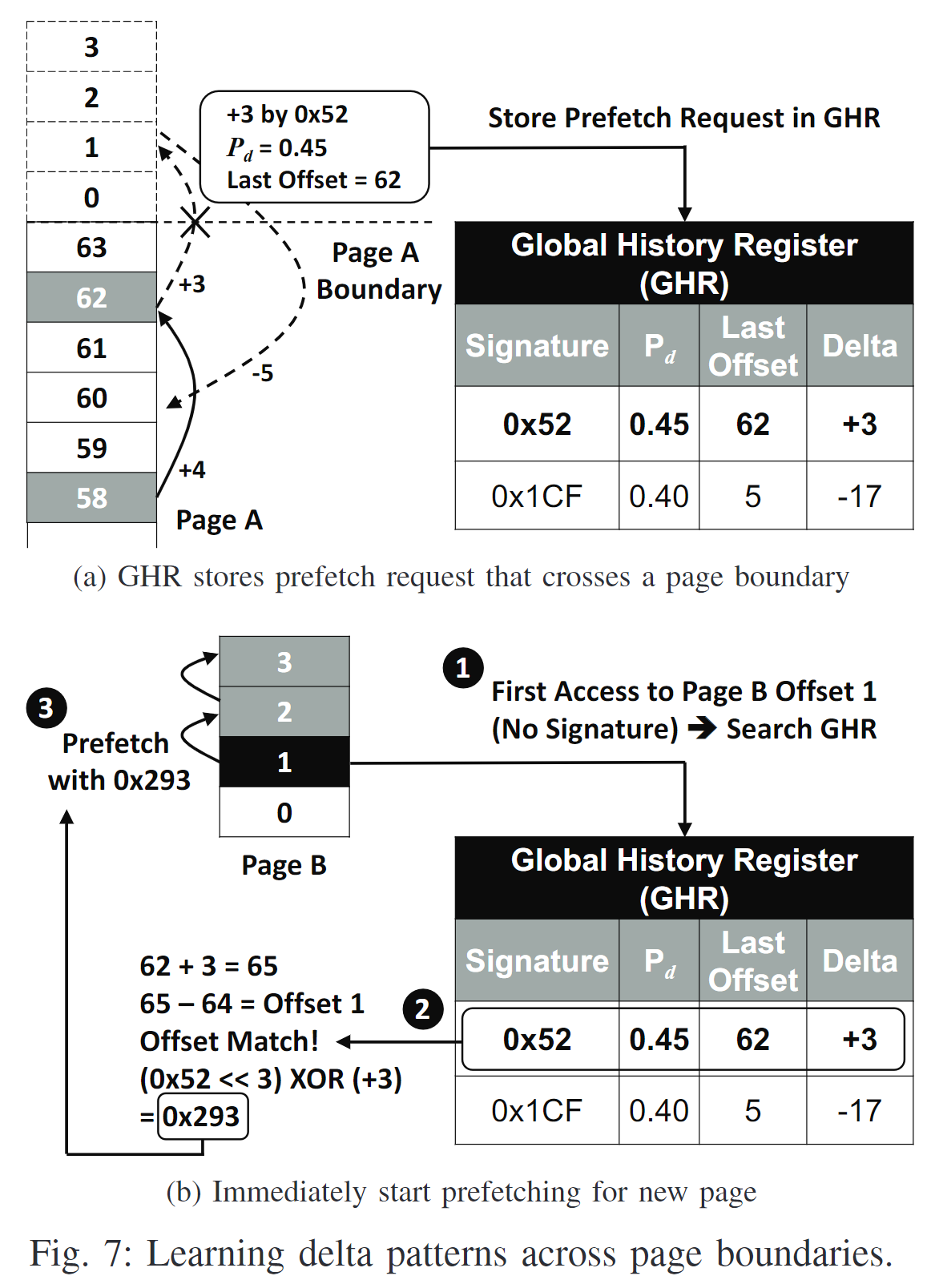
- A prefetch request goes beyond the current Page A --> Store in GHR
GHR可以存储8个entry,每个entry存储了当前的signature, path confidence, last offset, 以及delta。
- New page access
如果访问一个new page(ST miss), SPP会先在GHR搜索能跟当前访问match的GHR entry。
比如Figure7 (b)显示的,Last Offset + Delta - 64和当前对page B offset 1的访问对应。因此可以预测,Page B会产生一个对应0x52 signature的pattern
然后用0x52和delta(+3)产生一个Page B的新signature 0x293
4. Prefetch Filter
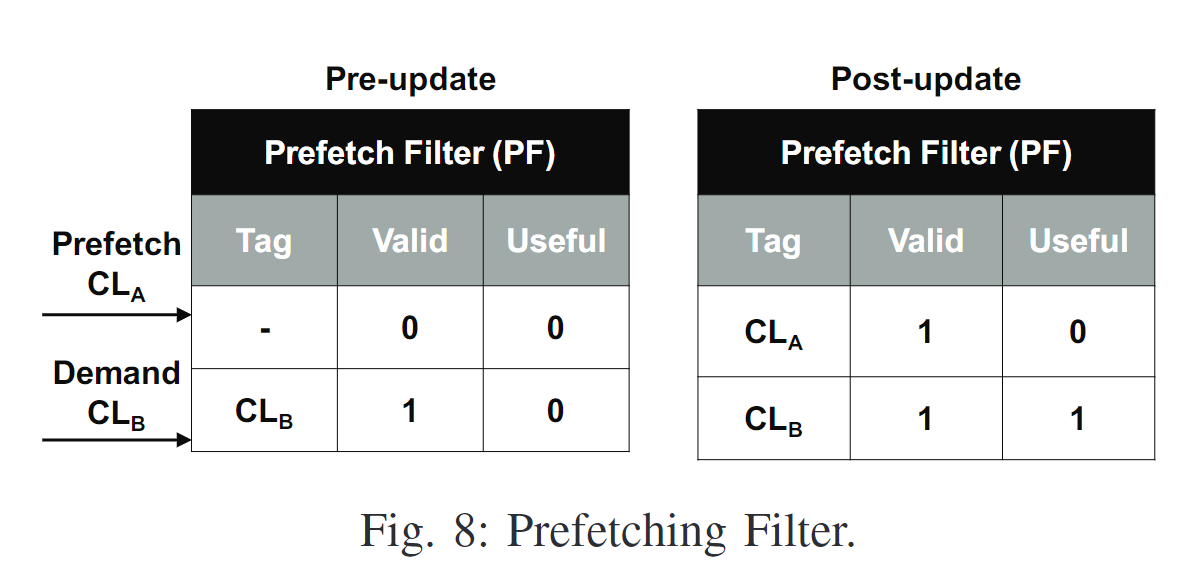
Prefetch Filter是一个direct-mapped filter, 记录当前prefetched cache lines
SPP在issue prefetch之前会先检查PF。如果PF中存在某个cache line, 那么说明这个line早就被预取了,SPP会丢弃这个redundant prefetch request。
在PF中为每个entry增加useful是为了SPP计算accuracy
SPP会记录两个global counter:记录prefetch request的总数, 记录 useful prefetch的数量。
在SPP issue一个没有被filter的prefetch request的时候会+1
在L2 demand requests hit PF的时候会+1。在PF中增加useful bit是为了防止同一个cache line加多次。
SPP + PPF
PPF_Design.svg
H11-Make Prefetch Great Again / Improve Data Prefetching: Perceptron-based Filter in gem5 on Vimeo
目的:SPP目前的confidence-based throttling机制很复杂。accuracy和coverage是两个此消彼长的因素,很难调节。PPF可以让SPP激进的发送请求,并且将其的一些无用的request过滤掉,达到兼顾coverage和accuracy的效果
Structure
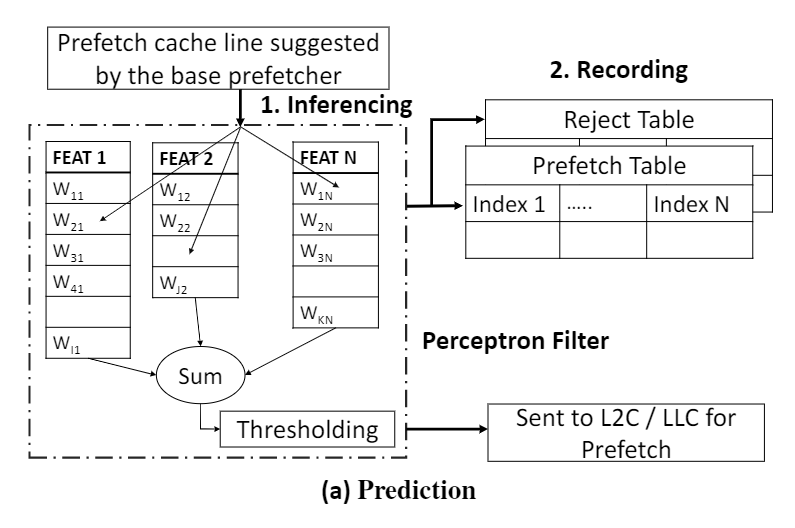
a. Perceptron
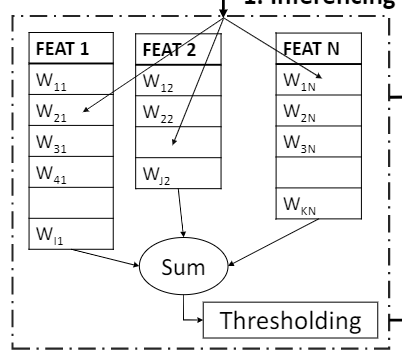
对于一个有N个feature的PPF来说,他包含
- N个table(存储权重)
- table里面的每个entry代表一个权重。权哥entry是一个5位的饱和计数器
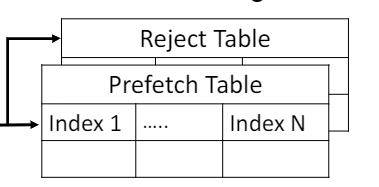
b. Prefetch Table & Reject Table
这两个Table中Prefetch Table记录了prefetch request的信息,Reject Table记录了不应该被prefetch的信息,这两个table被用来train perceptron
结构上,他们都是直接映射的结构,有1024个entry, 用addr的10位地址索引,6位做tag比较,entry中存储了各种feature相关的信息
Process
i. Interfencing
对于suggested prefetch request, 先通过perceptron中各种feature的weight计算出sum。将sum和两个threshold作比较:
-> prefetch into L2
-> prefetch into LLC
ii. Recording
过程中将认为应该issue到L2的prefetch的加入prefetch table, 将其他的request加入reject table
iii. Training
主要在两个时间点进行PPF training, 一个是demand request来的时候,另一个是cache eviction的时候。
Demand request来的时候,访问prefetch table更新权重,访问reject table更新权重
同样cache eviction的时候,也做权重的更新
DSPatch
性能表现
- 在75个不同的工作负载中,仅使用3.6KB的存储空间,DSPatch相对于一个PC-based stride prefetcher在L1缓存和SPP在L2缓存的激进基线提高了6%的性能(在内存密集型工作负载中提高了9%,最高可达26%)。
- 作为一个独立的预取器,DSPatch的性能略高于最先进的SPP(1%左右),且仅需SPP存储要求的2/3。
- SPP和DSPatch的使用结合了最先进的delta-based prefetching和bit-pattern-based prefetching的优点。通过同时优化覆盖率和准确性,DSPatch每增加2%的覆盖率只会增加1%的错误预测。最后,DSPatch+SPP的性能随着内存带宽的增加而扩展得很好,从SPP上升6%到DRAM带宽翻倍时上升10%
DSPatch Design
https://people.inf.ethz.ch/omutlu/pub/DSPatch_prefetcher_micro19-talk.pdf
The key goal of DSPatch is to dynamically adapt prefetch-ing for either higher coverage or higher accuracy depending onthe DRAM bandwidth utilization.
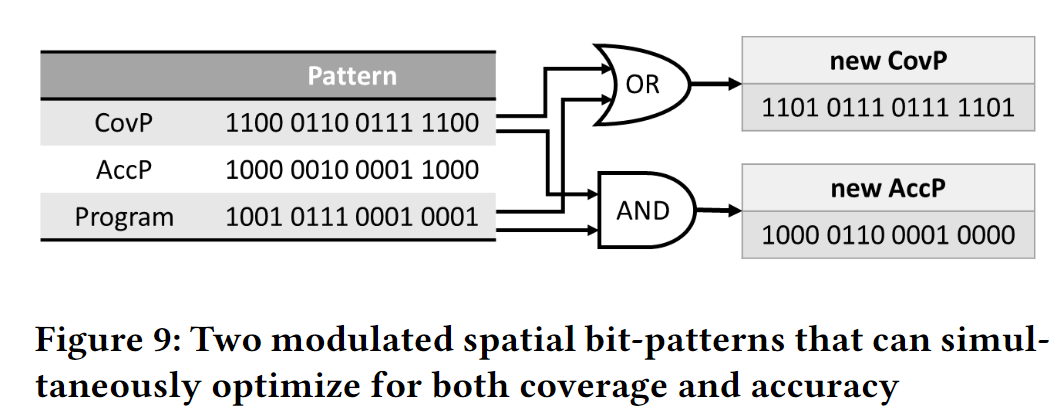
DSPatch为每个physical page学习两个pattern, 并将这两个pattern和PC based signature相联。这两个pattern分别为
- CovP: for higher coverage, 通过OR操作获得
- AccP: for higher accuracy,通过AND操作获得
Structure
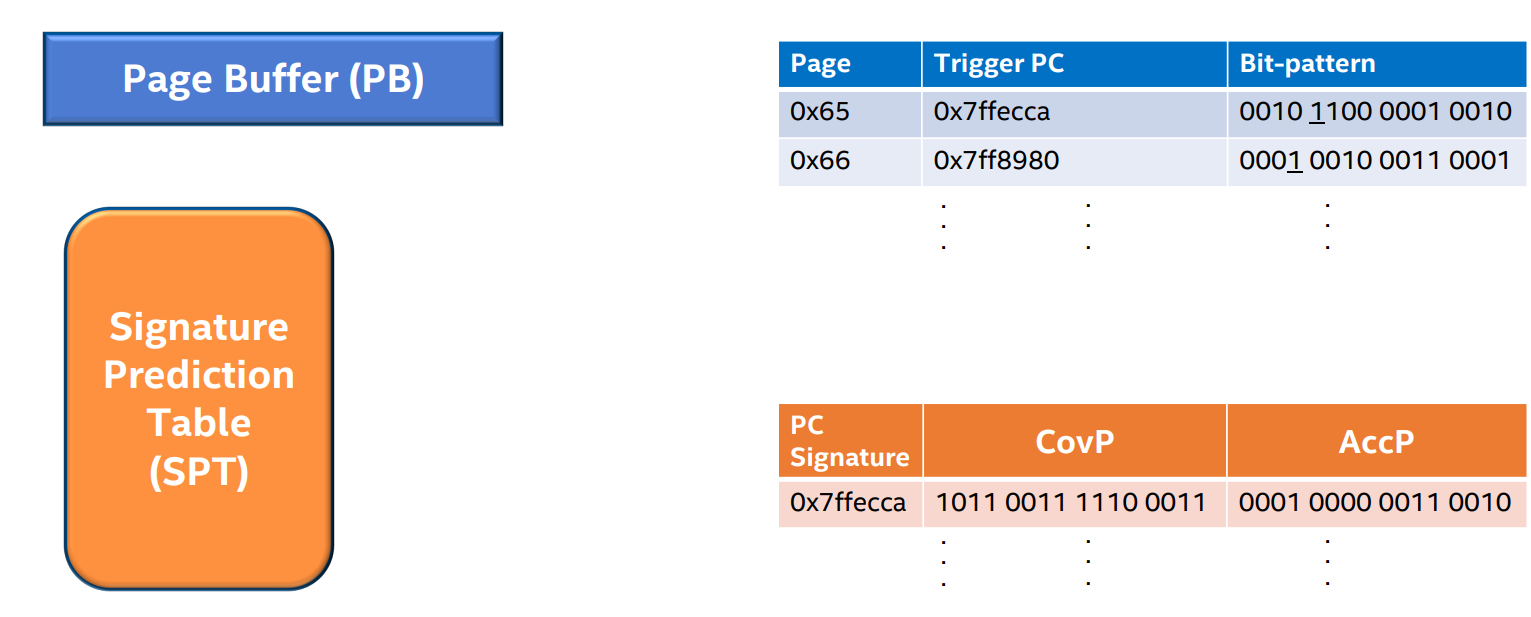
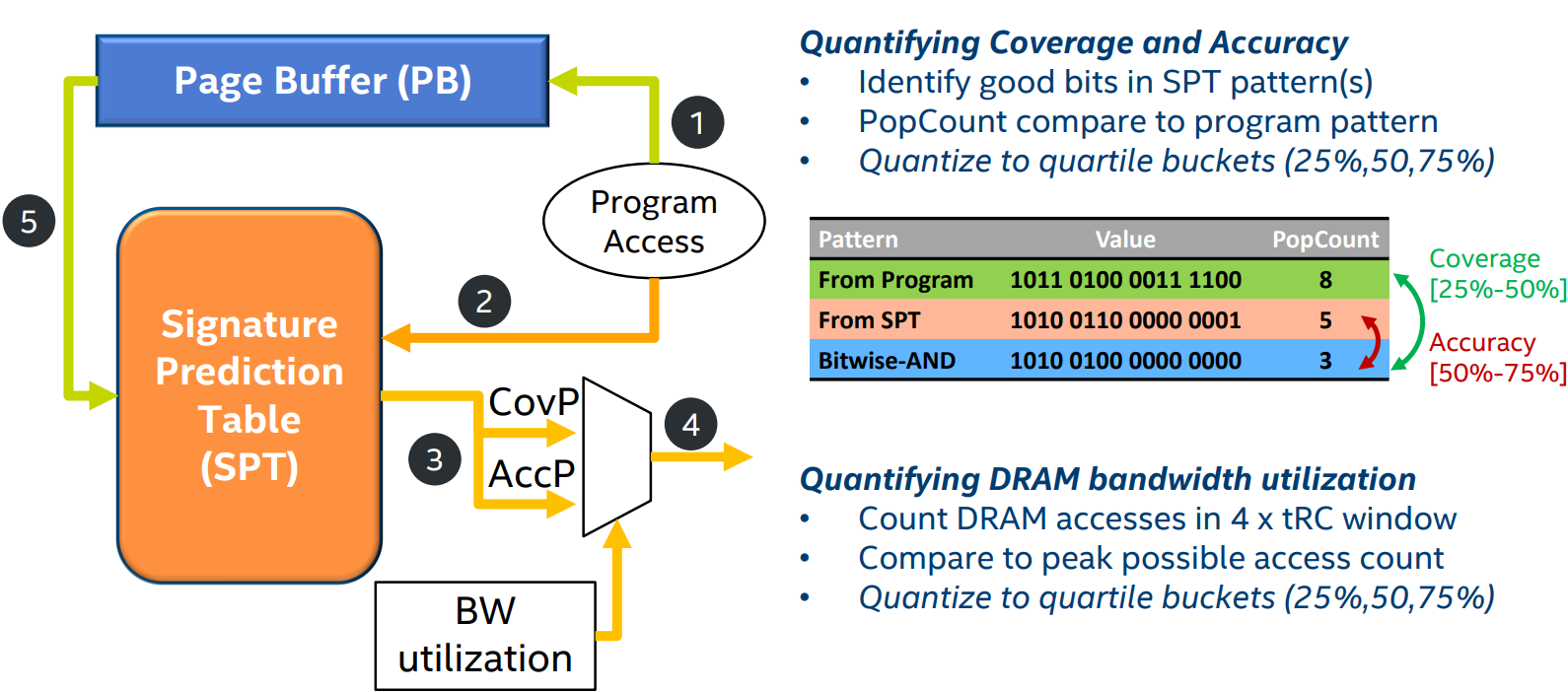
- Page Buffer (PB)
- 目的是记录当程序访问一个physical page的时候,记录spatial bit patterns

- 目的是记录当程序访问一个physical page的时候,记录spatial bit patterns
- Signature Prediction Table (SPT)
- 目的是存储CovP和AccP, 这两个pattern是从之前的访问中通过一定计算获得的
- 目的是存储CovP和AccP, 这两个pattern是从之前的访问中通过一定计算获得的
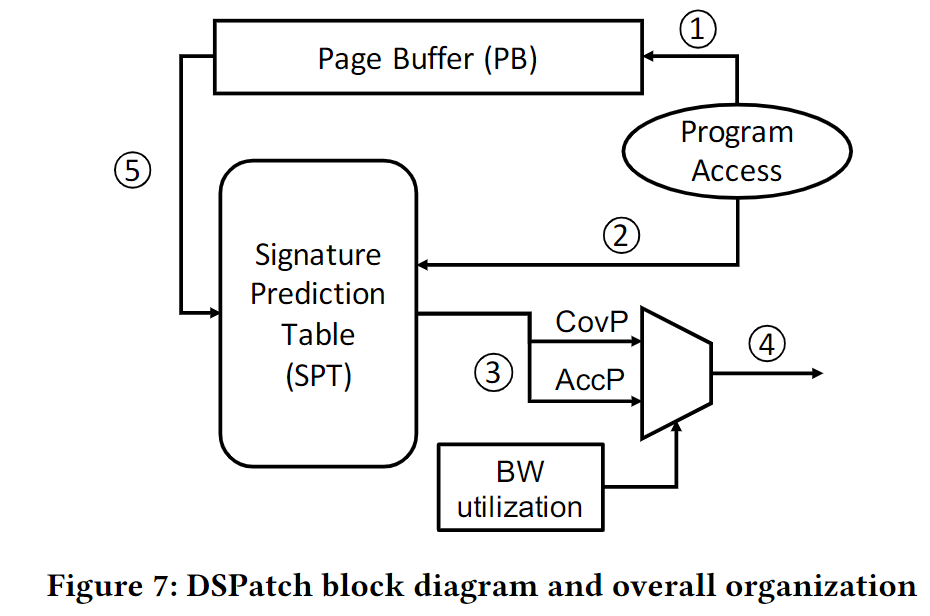
Overall Steps
- step 1: Each PB entry tracks accesses in a 4KB physical page and accumulates L1 misses in the page's stored bit-pattern
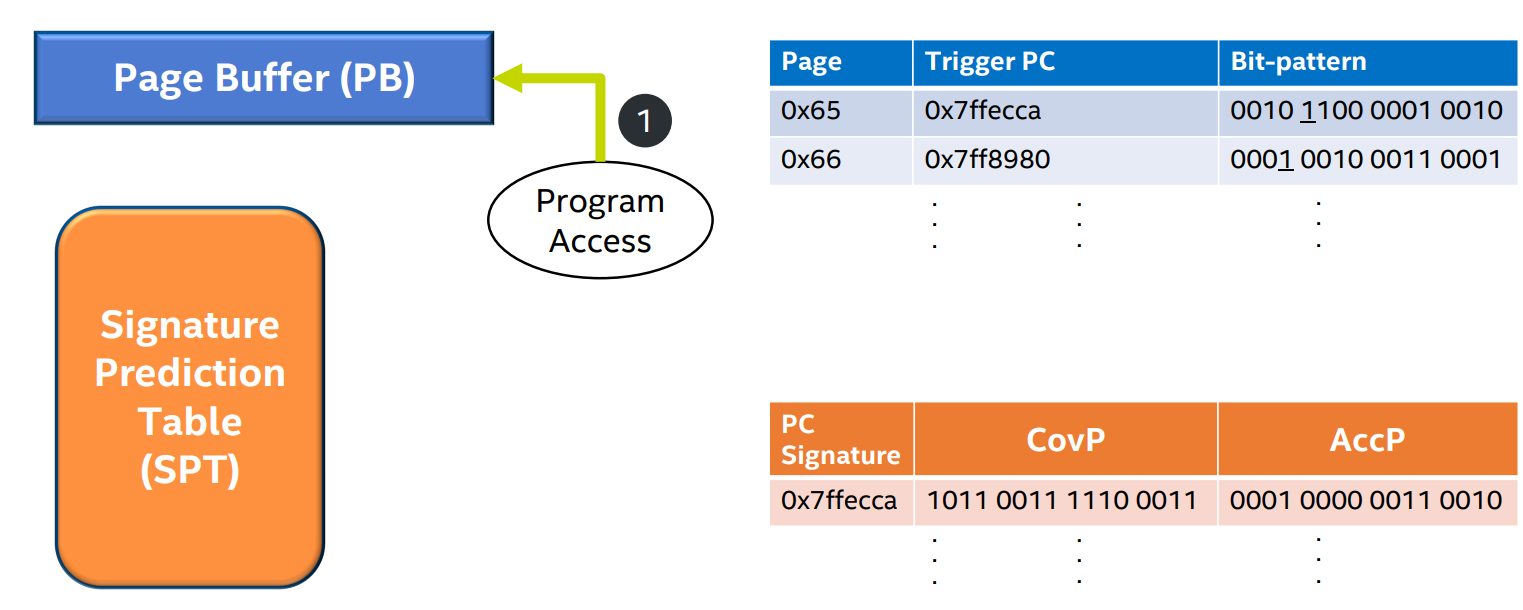
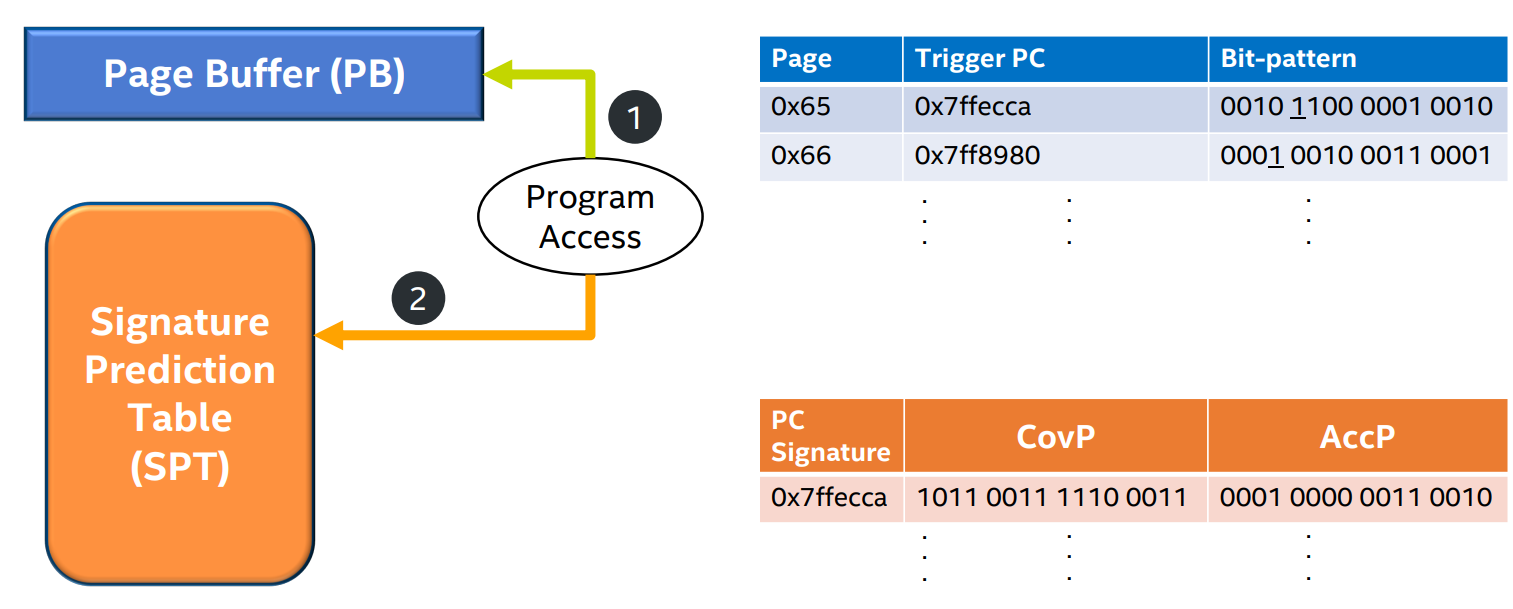
- step 2: The first access to each 2KB segment in the 4KB physical page is eligible to trigger prefetches.
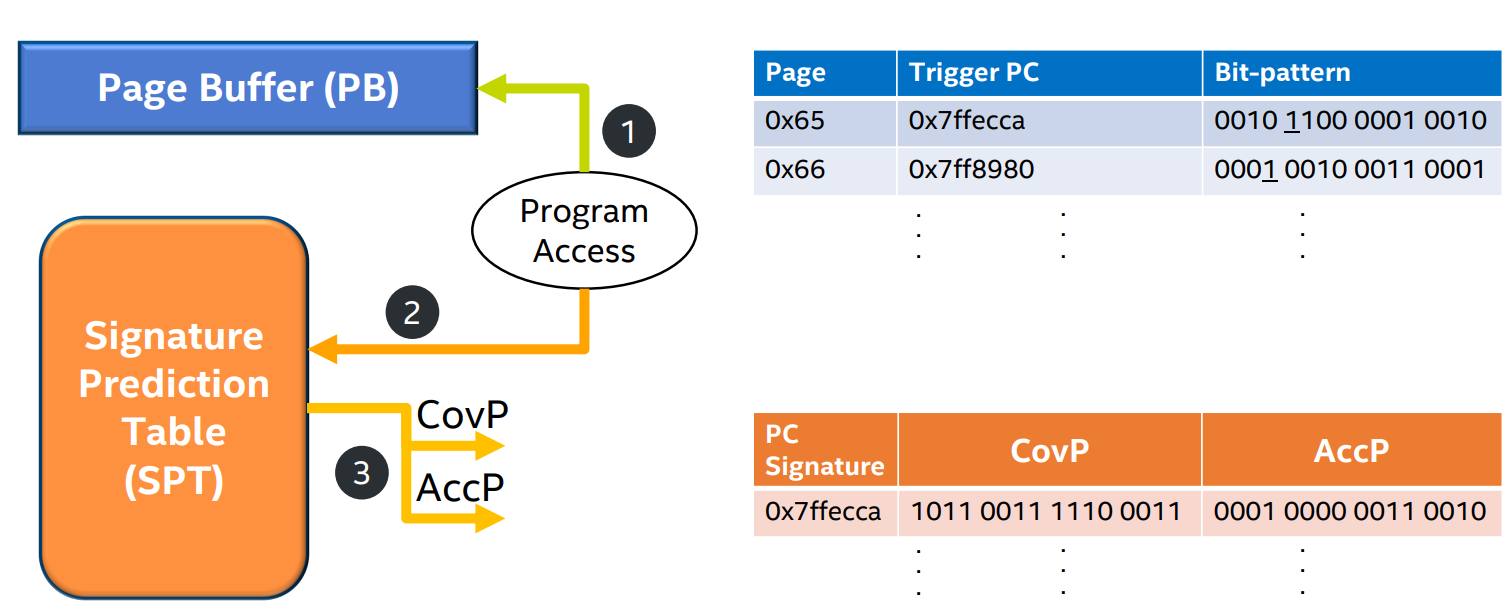
- step 3: The PC of this trigger access is stored in the PB entry and used to index into the SPT, which retrieves the two CovP and AccP bit-patterns and the measure of their goodness.
- step 4: Selection logic uses the memory bandwidth utilization measure to select a bit-pattern to generate prefetcher candidates. The selected bit-pattern is anchored(i.e. rotated) to align to the trigger access offset before issuing prefetches.
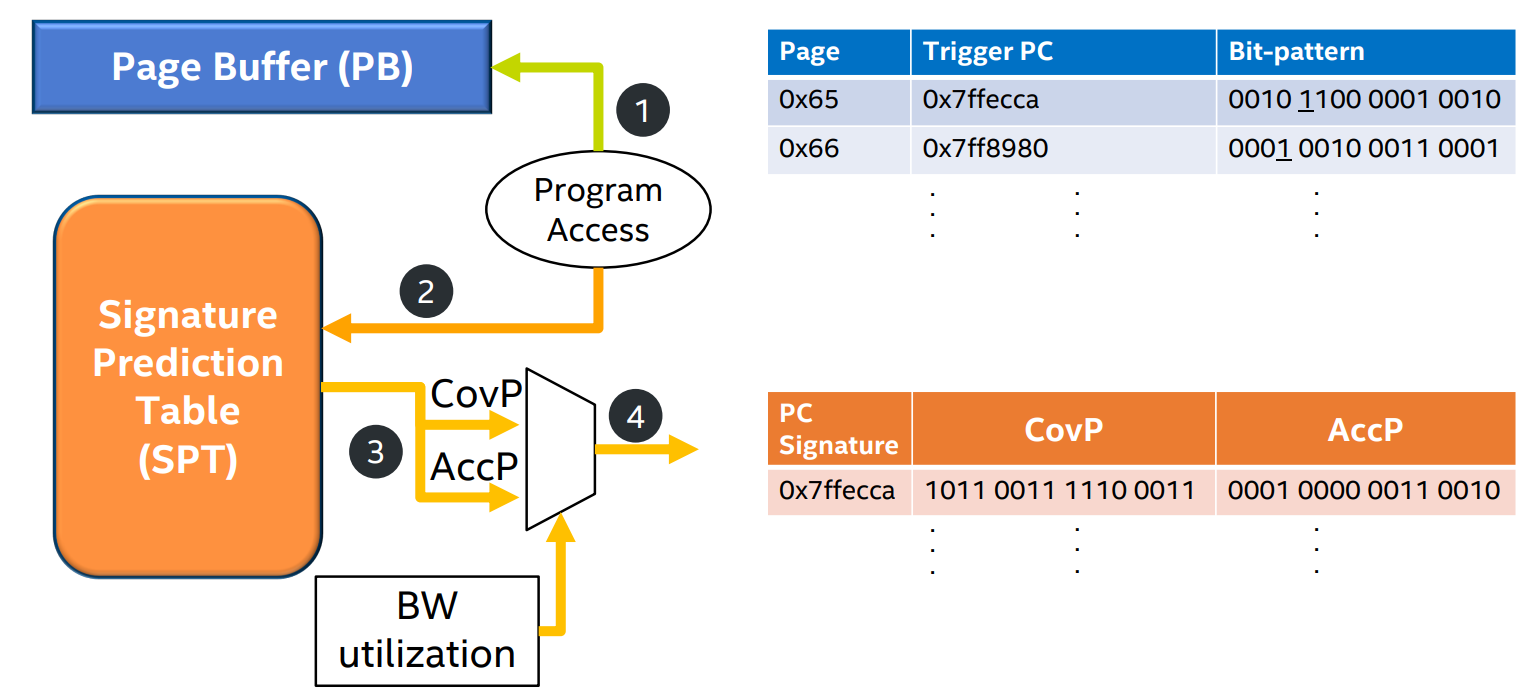
- step 5: On eviction from the PB, for each trigger (per 2KB segment), the stored bit-pattern is first anchored to trigger offset. Then, SPT is looked up using the stored trigger PC and the stored bit-patterns and the counters are updated.
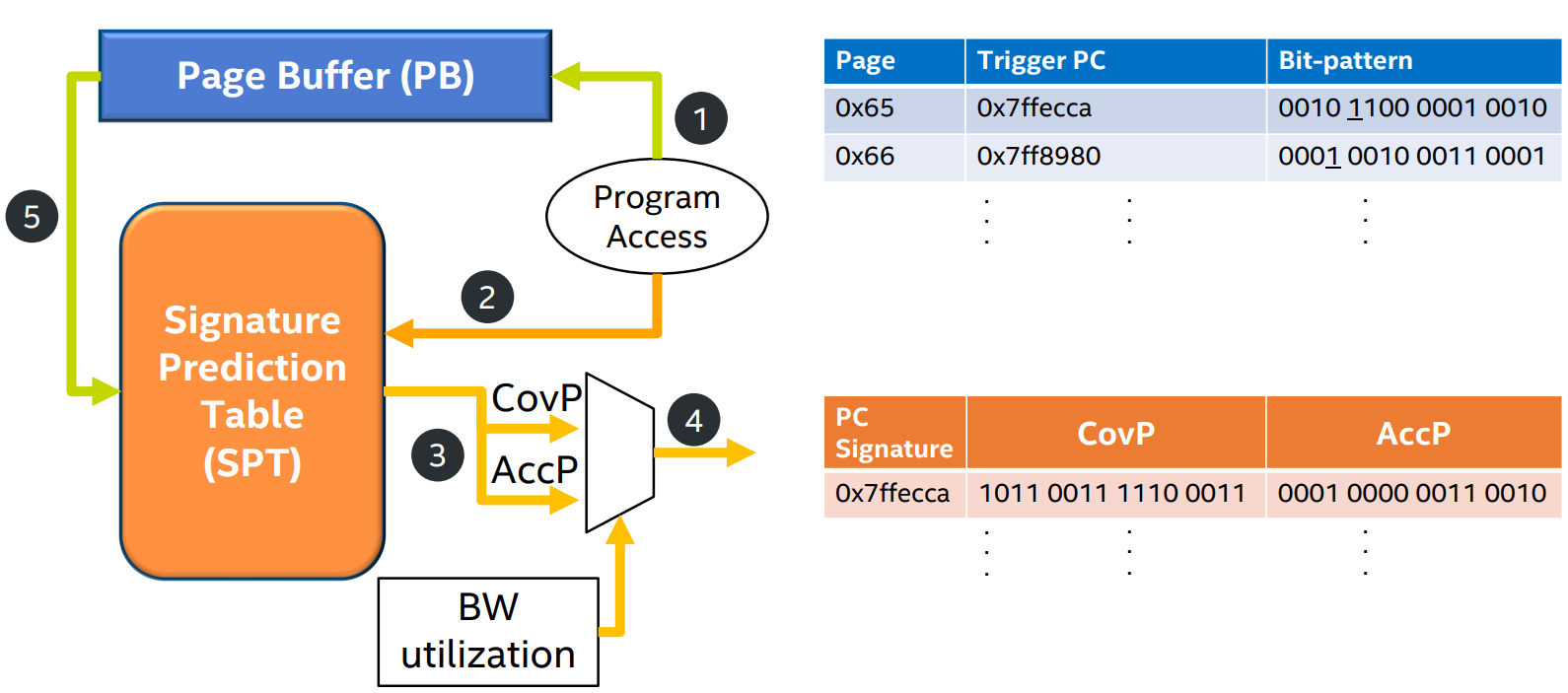
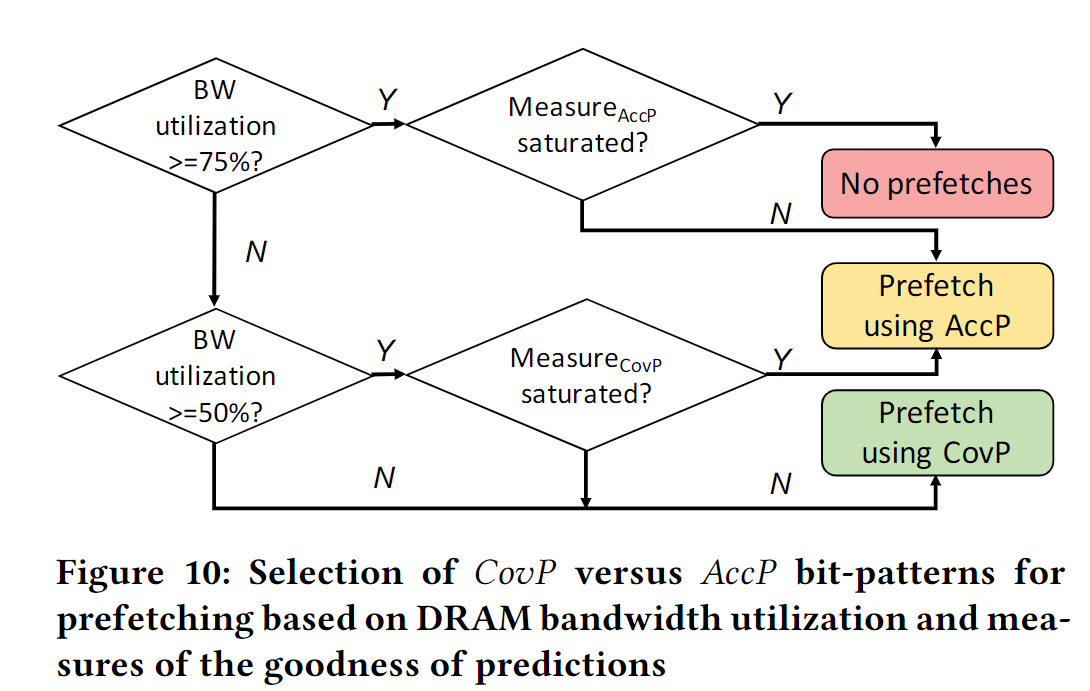
Tracking Bandwidth Utilization
文章提出了一个简单的方法来跟踪DRAM带宽利用率。
在每个内存控制器中维护一个计数器,记录每个内存周期内发出的请求数量。
当计数器超过一个阈值时,认为DRAM带宽已经饱和,此时应该使用偏向于准确率的bit pattern;
当计数器低于另一个阈值时,认为DRAM带宽有空闲,此时应该使用偏向于覆盖率的bit pattern。
Anchored Spatial Bit-patterns
DSPatch uses a program access representation that is robust against reordering of accesses in the processor and the memory hierarchy
Use spatial bit-patterns anchored to the trigger (i.e.,first) access to a memory region to capture all local and global deltas from the trigger. (所有都记录相对于在该page上第一个access也就是trigger access的偏移)
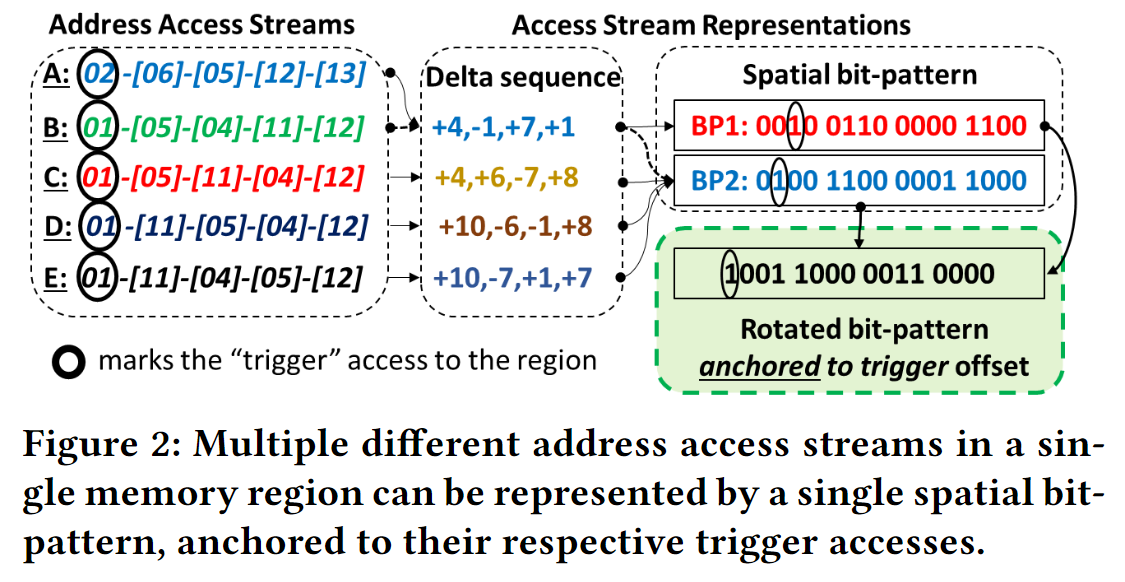
The Choice of Signature and Signature-Pattern Mapping
Quantifying Accuracy and Coverage
PopCount of the predicted bit-pattern gives the prefetch count (
PopCount of the access bit-pattern generated by the program gives the total number of accesses (
PopCount of the bitwise AND operation between the program bit-pattern and the predicted bit-pattern gives the accurate prefetch count (
Prediction accuracy:
Prediction coverage:
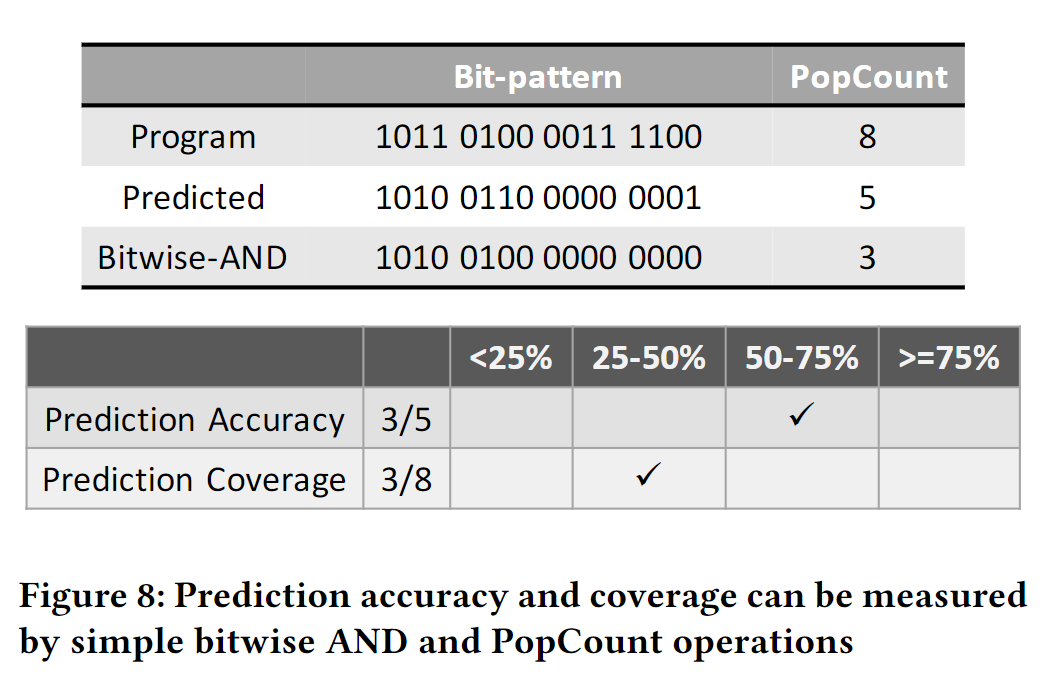
Modulated Dual Bit-patterns: Coverage-biased and Accuracy-biased
Coverage-biased Bit-pattern (CovP):
Accuracy-biased Bit-pattern (AccP)
IPCP Prefetcher
https://dpc3.compas.cs.stonybrook.edu/slides/bouquet.pdf
i. 四类prefetcher
1. Constant Stride (CS): only control flow
a. 目标
预取如下呈现的constant stride pattern

b. components
下图是constant stride (CS)下IP table的内容
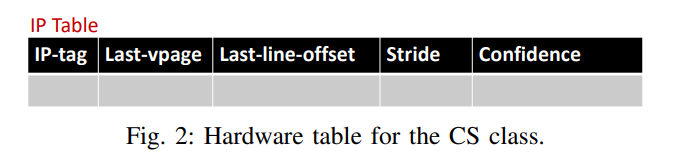
- 由IP来index和tag
- stride是用来记录constant stride的
- confidence来记录当前stride的置信程度。如果遇到了相同的stride, confidence增加,反之减小
- last_vpage存储了上一次访问 的virtual page的2个低位,用来检测page的变化。
- last_line_offset存储了上一次访问的cache line相对于page的offset
- last_vpage以及last_line_offset二者一起决定了stride的计算结果。比如last page是1,last_line_offset是63,当前page是2,line offset是0,那么当前stride就是(0-63)+64(2-1)=1
c. process
- Training phase
- IP会持续training直到confidence达到某个threshold
- Thained phase
- IP获得足够的confidence后进入trained状态
- 发起perfetch请求
- prefetch addr = (cur cacheline addr) + k * (learned stride), 其中k取1到prefetch degree的值
- confidence低于threshold进入training状态
2. Complex Stride (CPLX): control flow coupled with data flow
a. 目标
在stride不断变化的情况下取得比较好的预取效果

b. components
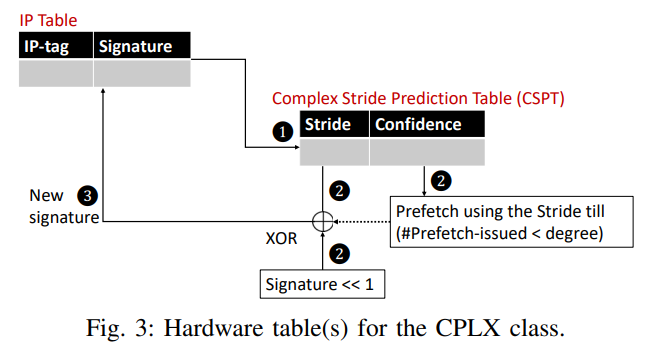
- IP table
- 同上的IP table, 加入一个n位的signature, 记录前n个stride hash之后的结果
- CSPT
- 由signature索引
- stride是预测的当前的signature下,下一次访问的stride是多少
- confidence代表这个预测的stride的置信程度
c. Process
- Training phase
- IP对应的signature索引到CSPT
- 如果CSPT中的stride和当前stride一样,则增加confidence, 反之减少
- 更新IP table中的signature
- Trained phase
- 用上述更新过的signature再去访问CSPT,如果对应的stride confidence足够高,则发送预取请求
- 在prefetch degree下,通过1,2,3步不断发射预取
d. CPLX与SPP的区别
- 关注的点不一样
- SPP关注某一page的访问
- CPLX是关注某一IP
- access pattern不一样,以下几种情况CPLX会好一点
- The memory accesses (for a given IP) are sometimes not in the powers of two (memory layout in data structures across cache lines), causing an nonconstant stride pattern.
- 例子是consider a cache line of 8 bytes, and if every 12th byte is accessed, the accesses create strides as follows: byte addresses: 0, 12, 36, 48, 72; cache line aligned addresses: 0, 1, 3, 4, 6; strides: 1, 2, 1, 2
- 对于多重循环的访问
- An outer loop could make constant stride accesses (can be easily captured by the CS class).
- However, an inner loop could make different stride accesses (depending on the strides of the outer loop), thus causing bumps in the stride pattern. An IP based CPLX can exploit this pattern.
- The memory accesses (for a given IP) are sometimes not in the powers of two (memory layout in data structures across cache lines), causing an nonconstant stride pattern.
- global & local
- SPP关注的是global pattern
- CPLX关注的是local pattern
3. Global stream (GS): control flow predicted data flow
a. 目标
b. components
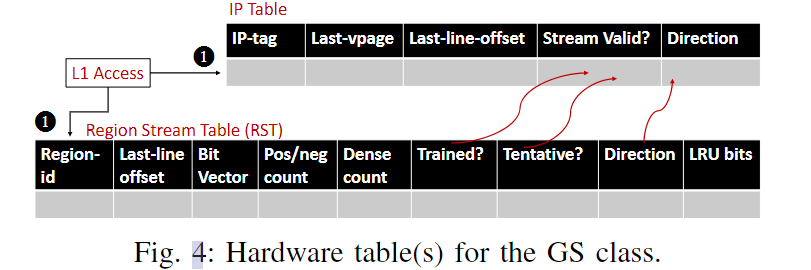
- IP table
- IP tag与索引
- stream-valid
- direction
- Region Stream Table(RST)
- 记录每个region以及他们的访问,一个region大小为2KB
- 32-bit bit-vector: 记录该region中32个cache line的访问情况。如果该region中的某个cacheline被第一次访问,对应的bit会置1,同时dense counter加1
- dense counter:记录不同的cache line的访问次数。当dense-count超过了75%,表示这个region已经训练完成
- last line offset: 记录region中最后一次访问的offset
c. Process
- Training Process
- 如果一个新的region被访问,则在RST中分配一个新的entry。如果该region中的某个cacheline被第一次访问,对应的bit会置1,同时dense counter加1(不是第一次访问的话不会增加)。
- 如果dense counter超过75%,则所有访问该region的IP成为GS IP。trained bit被置1
- RST使用n-bit饱和计数器来决定stream的direction (pos / neg count)。这个计数器被初始化为
。通过找到两个连续访问之间的差值计数(last-line-offset起作用),如果是正的插值,则加1,负的插值则减1 - 如果GS IP到了一个新的region,则通过last-vpage和last-line-offset看他之前访问的region。如果之前访问的region是dense的(trained bit set), 那么将新region的RST entry的tentative bit置1。
- Trained Process
- demand access来的时候,检查RST entry的trained bit和tentative bit, 如果有一个set了,说明这个IP属于GS IP
- Set IP table中的stream-valid和direction
- GS IP根据trained direction prefetch接下来的prefetch degree个cache line
4. Next line
如果CS, CPLX, GS不是的话,则启用NL prefetcher。当MPKI太高的时候,不要开启NL Prefetcher
ii. IPCP整体架构
1. IPCP at L1
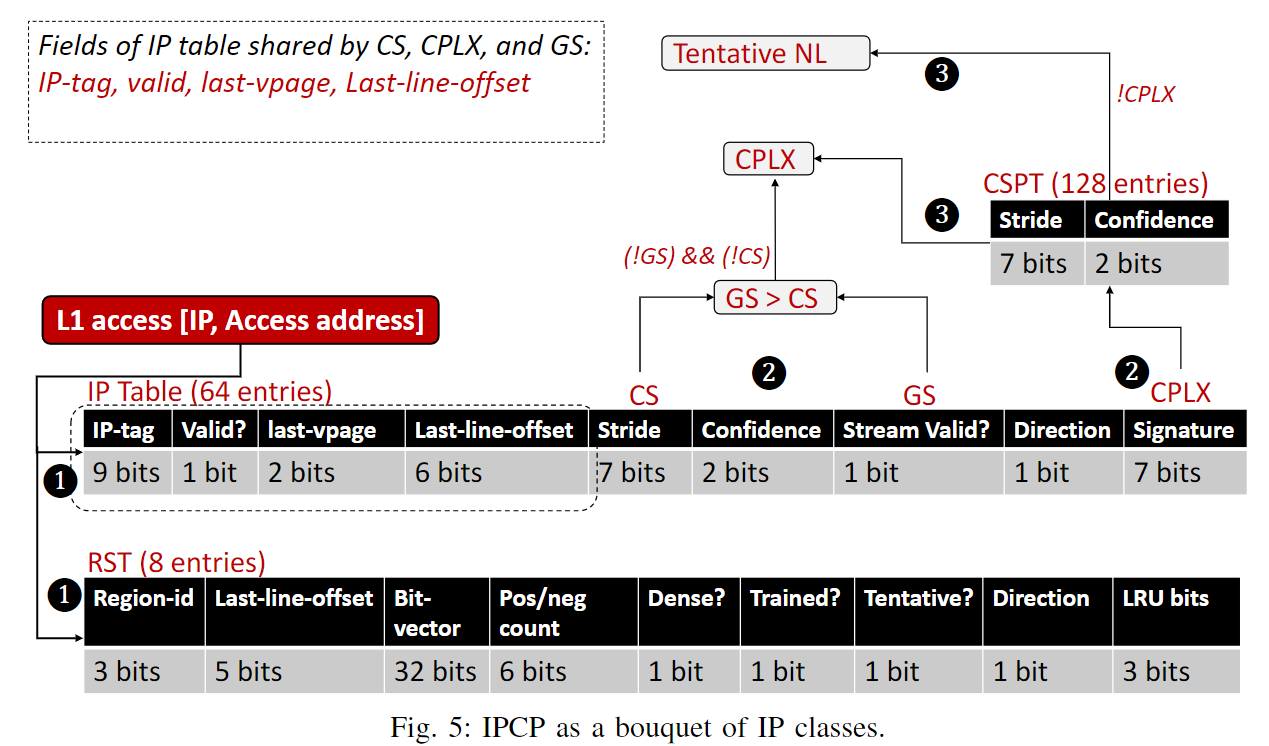
a. Components
- IP Table
- Shared: IP-tag, Valid, last-vpage, last-line-offset
- for CS:
- Stride
- Confidence
- for CPLX:
- Signature
- for GS:
- Stream valid
- direction
- RST
- CSPT
关于IP table的替换问题:
When an IP is encountered for the first time, it is recorded in the IP table and the valid bit is set.
When another IP maps to the same entry, the valid bit is reset, but the previous entry remains active.
If the valid bit is reset when a new IP is seen then the table entry is allocated to the new IP and the valid bit is set again, ensuring that at least one of the two competing IPs is tracked in the IP table.
b. Process
- IP table hit, 则IPCP同时检查CS/CPLX/GS。同一时间,IP可能不属于任意一个class, 或者属于多个class。同时,检查RST并且训练
- IPCP看IP属于CS还是GS。如果都属于,那么IPCP会优先选择GS
- IPCP不属于CS和GS,看是否属于CPLX。
- 如果CPLX的confidence不高,则根据MPKI选择NL Prefetcher
整体上,优先级为
c. 一些设计问题
- Prefetch Degree
- GS: 6
- CS & CPLX: 3
- Filter
- Use a small recent-request filter (RR filter, 32 entry) to track recently seen tags.
2. IPCP at L2
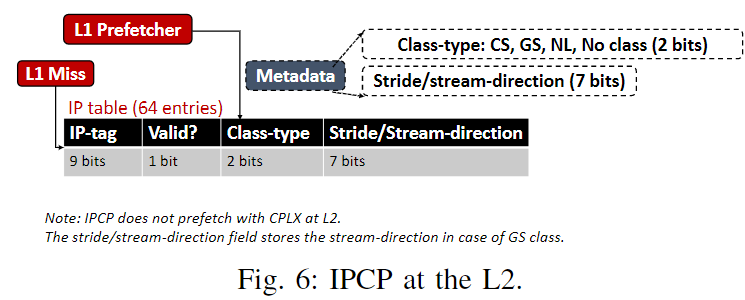
IPCP at L2没有CPLX, 因为测出来没啥用
a. components
- IP table
- IP tag, IP valid bit
- 2-bit class type
- 7-bit stride/direction
b. Process
- Metadata Decoding
use the L1 prefetch requests to communicate the IP classification information to the L2 prefetcher by transmitting lightweight metadata along with the prefetch requests.
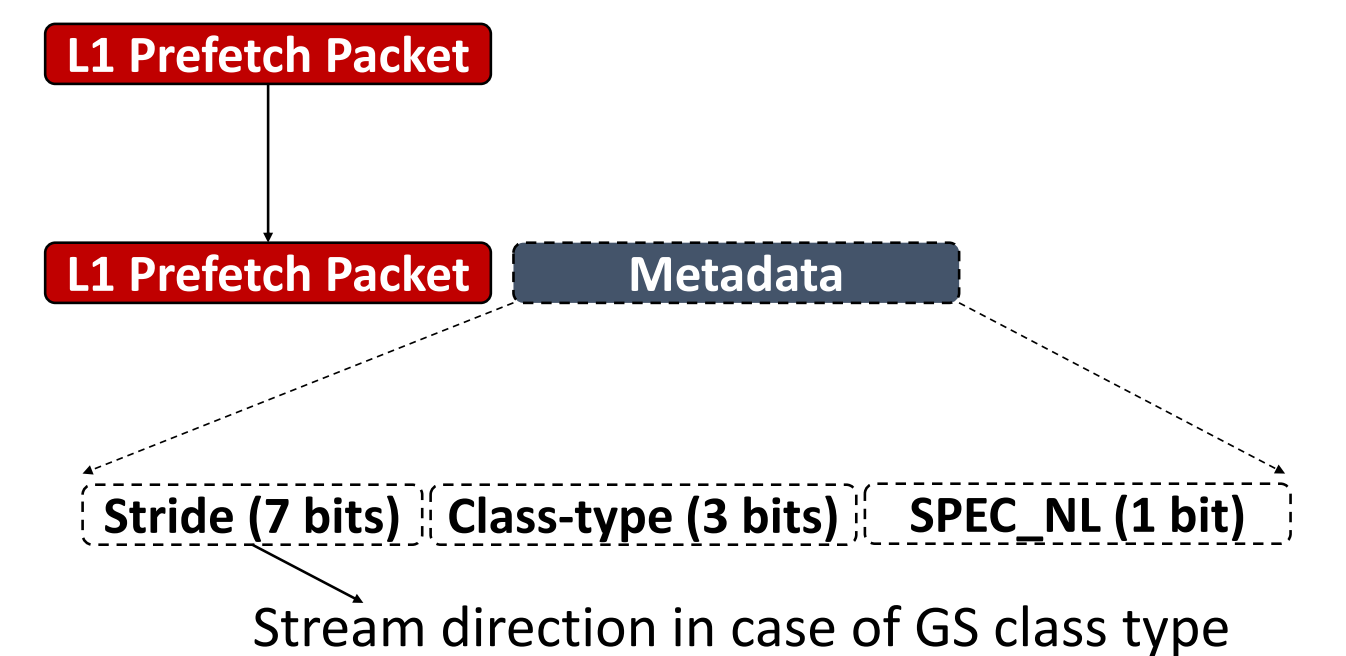
- Prefetch
- L2 demand access, 访问L2 IP table
c. 一些设计问题
- Prefetch Degree
- GS: 4
- CS: 4