Stride Prefetcher
1. Stride Pattern
- Definition: a sequence of memory accesses in which the distance of consecutive accesses is constant (e.g., {A, A + k, A + 2k, . . . })
- Source:
- programs with dense matrices and frequently come into sight when programs operate on multi-dimensional arrays
- pointer-based data structures when memory allocators arrange the objects sequentially and in a constant-size manner in the memory
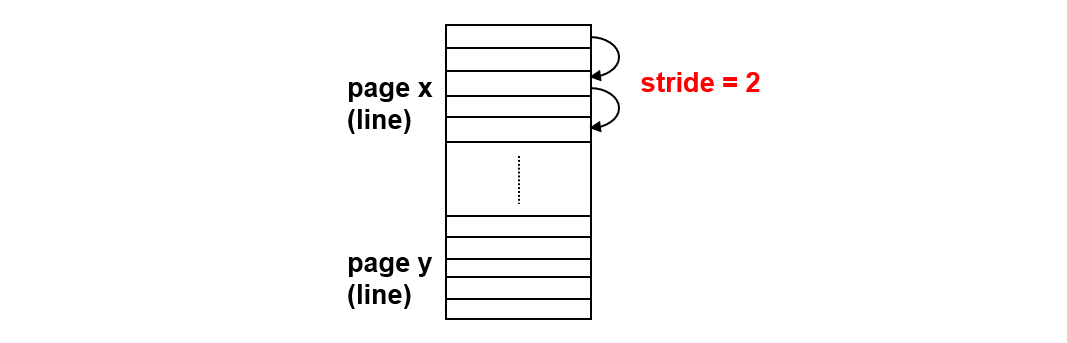
2. Stride Prefetcher
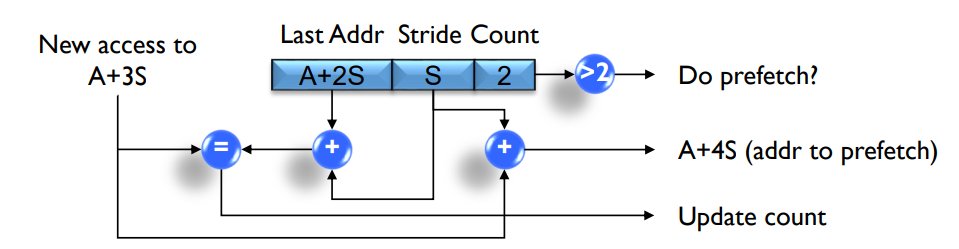
3. IP-based Stride Prefetcher
- SC'91 An effective on-chip preloading scheme to reduce data access penalty
- gem5/stride.hh at stable · gem5/gem5 · GitHub
- Stride Prefetcher code reading
Stride Prefetcher检测所有指令之间的stride关系(global)
IP-based Stride Prefetcher检测每条指令前后访问之间的stride关系(local)
3.1. Main Components
- RPT(Reference Prediction Table)
- 存储PC tag(用于匹配PC), last addr(用于计算stride), stride, count(置信度)
3.2. Process
- On Access, check RPT
- 匹配RPT entry, 如果stride和RPT entry一样,count++, 否则count--
- 如果count比较高,则进行prefetch
- 假设当前访问addr是A, stride是k, prefetch depth是3,则prefetch {A+k, A+2k, A+3k}
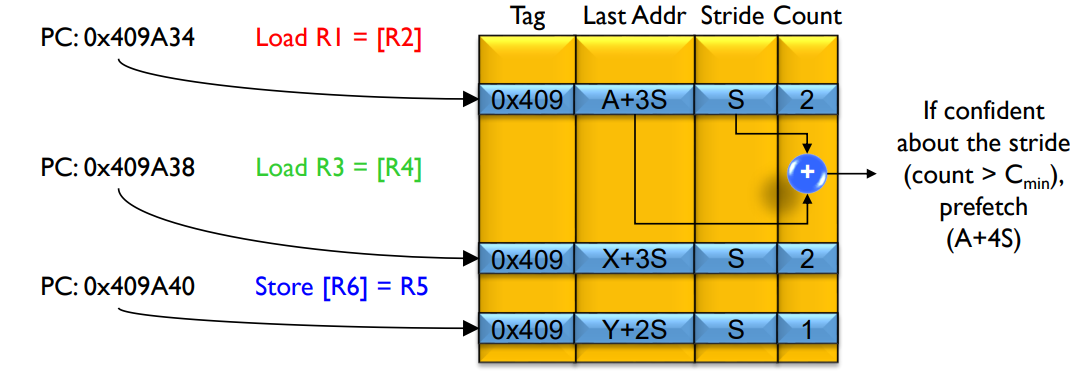
- 假设当前访问addr是A, stride是k, prefetch depth是3,则prefetch {A+k, A+2k, A+3k}
4. AMPM (access map pattern matching)
- ICS'09 Access Map Pattern Matching for High Performance Data Cache Prefetch
- slides
- gem5/access_map_pattern_matching.hh at stable · gem5/gem5 · GitHub
- AMPM code reading
总体上AMPM是一个检测很多stride的stride prefetcher
AMPM认为以前的prefetcher有几个关键问题(09年的时候)
- prefetcher只能检测比较简单的pattern, 所以coverage很低(比如stride prefetcher只能检测constant stride)
- 在CPU使用了比较大的优化时,比如out-of-order execution, memory访问被打乱,一些prefetcher无法应对这种乱序(比如GHB-based prefetcher, 按访问顺序记录memory access)
- ...
AMPM能够比较好的处理这些问题
- AMPM会检测一个范围的stride, 扩大了pattern检测的范围,有比较好的coverage
- AMPM在记录history时是通过memory region的bit pattern来记录的,因此不会受访问顺序影响
4.1. Main Components & Process
a. a memory access map
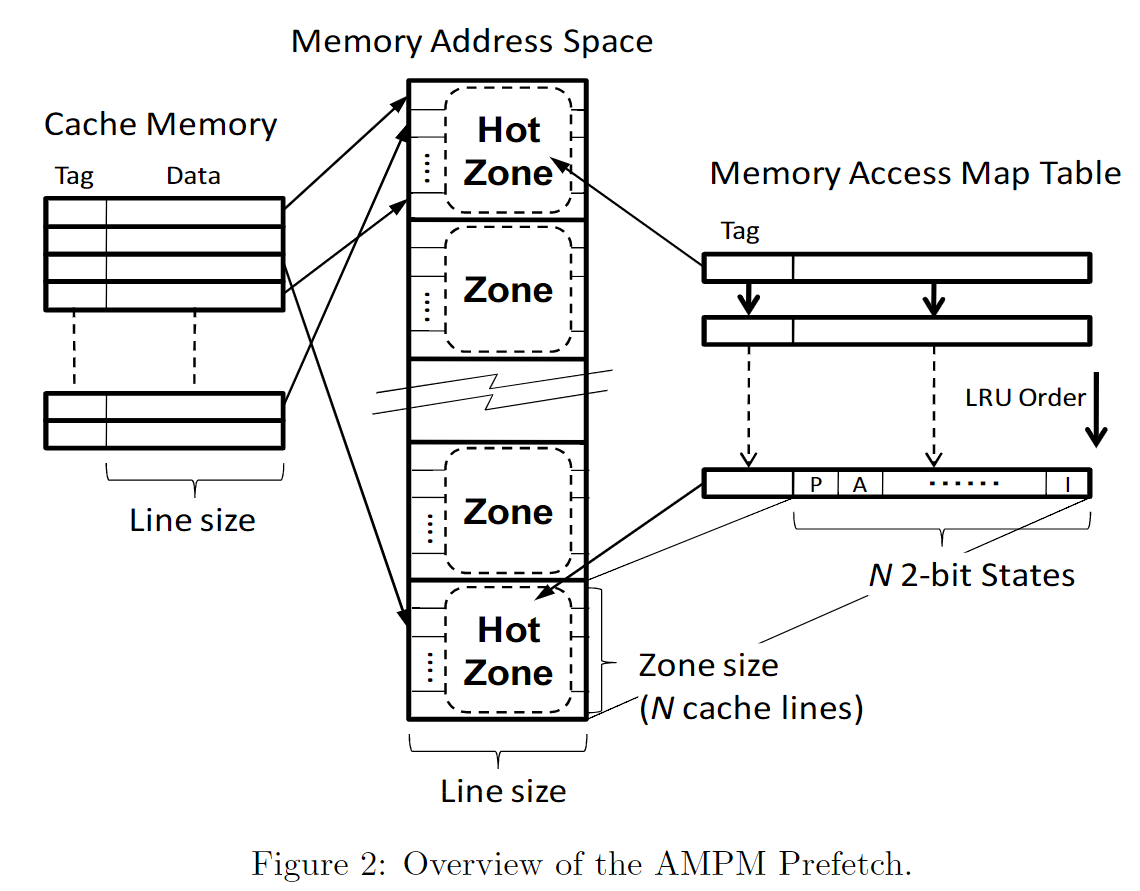
memory access map是一个bitmap的形式,其中的每个field都是一个状态机(访问与否,prefetch与否)。
AMPM将Memory划分成一个一个的zone, 比如2KB划分一个zone。
每个zone可以对应一个memory access map entry。zone中的每个cache line会对应到memory access map中的一个位置,对应该位置的一个状态机。
其中状态机的状态转换如下图所示
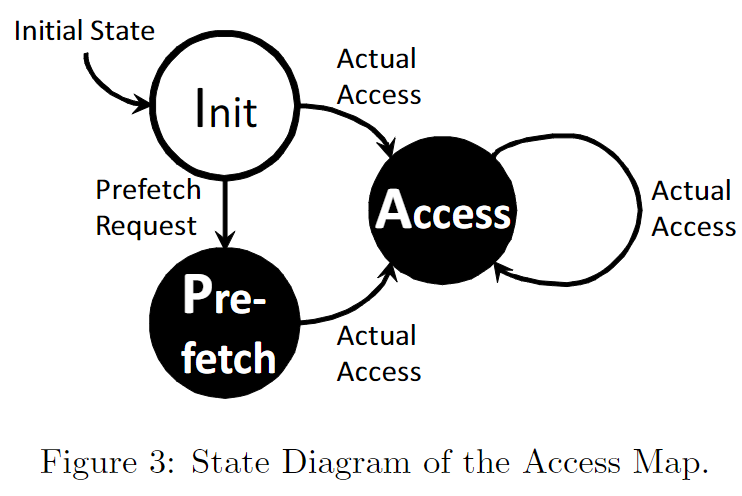
b. prefetch generator
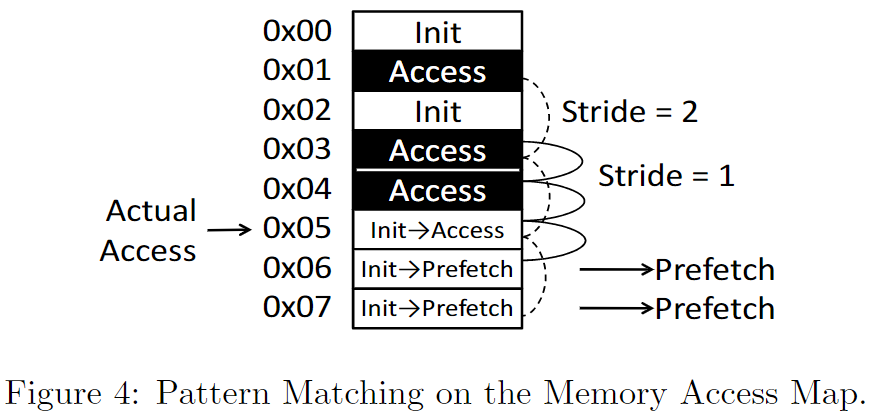
产生prefetch candidates的过程中,3个连续的zone的memory access map entry会被读入(前一个zone, 当前zone, 后一个zone),构成一个更大的memory access map。在这个map的基础上,pattern matching logic遍历stride, 生成一些可能的prefetch requests。
stride match的逻辑如下:
首先是一些变量名约定
t: request addr
N: the number of cache lines in one zone
k: stride
对k进行一个区间的遍历。hardware pattern matching logic同时检测memory access map中t+k, t+2k, t+2k+1的状态(k=0,1...N/2-1)。
如果t+k,t+2k(或者t+2k+1)处于Access state, 那么-k是一个可能的stride, t-k会成为一个prefetch candidate
如下是一个例子
0x1, 0x3, 0x4已经被访问了
当前0x5被访问
prefetch generator生成两个candidates
- 0x7 (模式为0x1, 0x3, 0x5)
- 0x6 (模式为0x3, 0x4, 0x5)
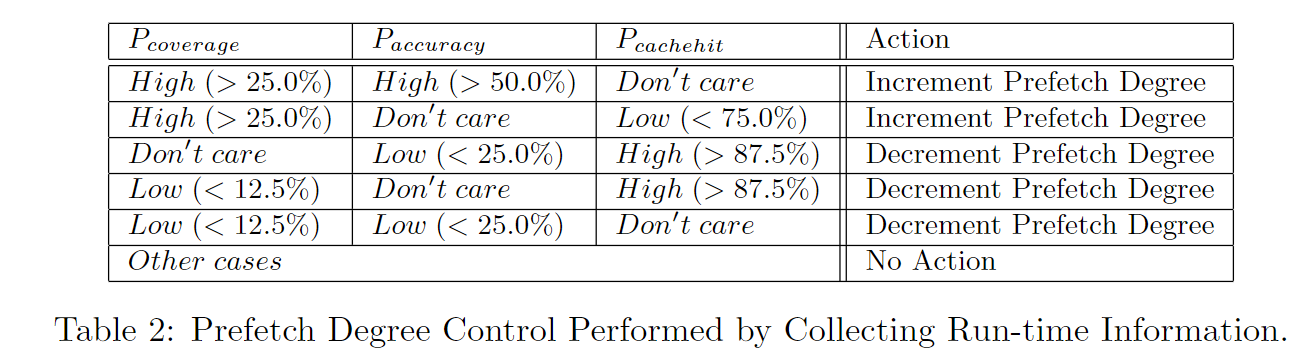
4.2. Prefetch Degree Control
AMPM在工作过程中会动态调节prefetch degree
AMPM通过如下表格中的4个统计数据来评估预取的有效性, 这些统计数据是通过memory access map中的状态转换得出的
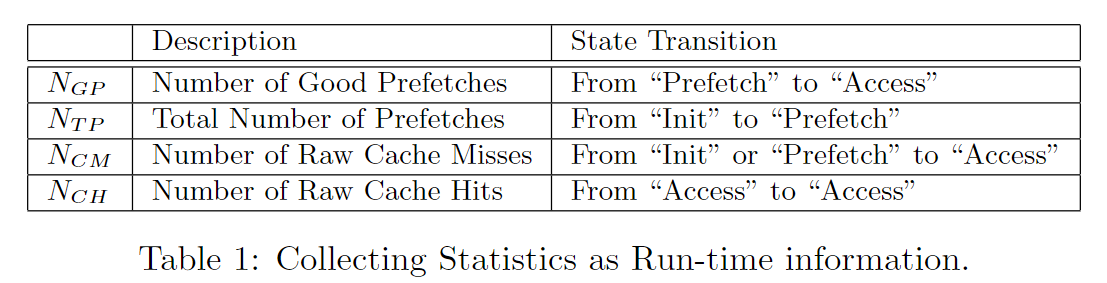
每个一个epoch时间,更新统计数据,通过上述统计数据进行计算
- prefetch accuracy: good prefetch / total prefetch
- prefetch coverage: good prefetch / cache miss
- cache miss ratio
- off-chip mem requests
下面是prefetch degree更新的逻辑
4.3 Overhead
a. Storage
memory access table的map array如果要hold N个states的话,size为2N(每个状态机2bits)。tag array会hold address的tag和LRU info。
当AMPM使用48位地址,hold 64个states, 256个map以及8-way set-assoc和128B cacheline时,storage为
256 maps * ((2 bits * 64 states)) + 35 bits (tag) + 3 bits (LRU)) = 42496 bits (~5.2KB)