Primer
1. Replacement policy主要关心的问题
- 插入策略(Insertion Policy):当新行被插入缓存后,缓存替换策略该如何初始化该行的替换状态(replacement state)?
- 晋升策略(Promotion Policy):当缓存行被命中后,缓存替换策略该如何更新它的替换状态?
- 衰老策略(Aging Policy):当一个与其相竞争的行(competing line)被插入或者晋升时,缓存替换策略该如何更新该行的替换状态?
- 驱逐策略(Eviction Policy):在给定固定数量的选项间,替换策略应该选择驱逐哪个缓存行?
2. A Taxonomy of Cache Replacement Policies
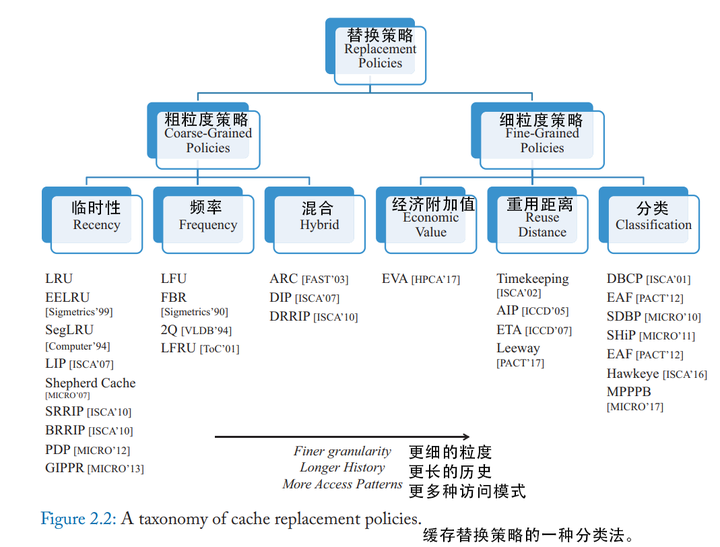
2.1 Coarse-grained policies
粗粒度策略在将缓存行插入缓存时,对任何行的处理都是相同的。它们主要是通过观察resue行为来区分cache-friendly line, cache-averse line
根据如何区分cache-resident lines, 可以分成三类
- recency based
- frequency based
- hybrid
2.2 Find-grained policies
细粒度策略会在插入行(至缓存)时就对它们进行区分。它们通过根据行之前的生命周期的信息来进行这些区分。例如,如果一个行在过去没受到任何命中,则可以以较低的优先级插入该行。
- classification-based
- reuse distance-based
2.3 Design Considerations
- 粒度(Granularity):在插入时,缓存行时以什么粒度进行区分的?是所有缓存行都一视同仁,还是根据历史信息给它们分配不同的优先级?
- 历史(History):替换策略在决策时利用了哪些,多少历史信息?
- 访问模式(Access Patterns):替换策略对某些访问模式的针对性如何?它对访问模式的变化,或不同访问模式的混合是否、有多敏感?
3. Coarse-Grained Replacement Policies
3.1 Recency-based Policies
a. LRU
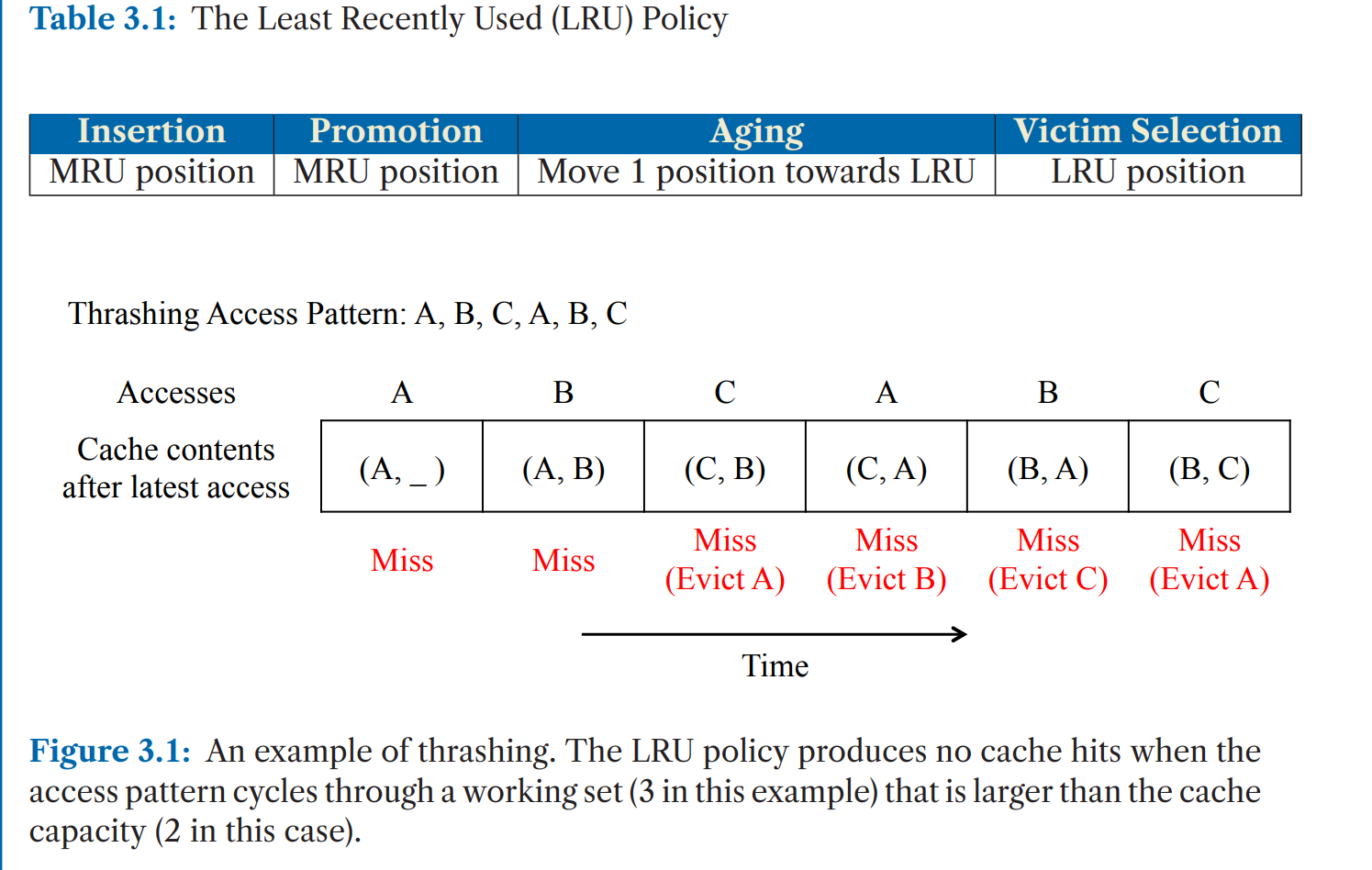
- good case
- temporal locality比较好的时候
- bad case
- application working set > cache size (上图中,cache为2,working set为3,产生thashing)
- scans(older line更有可能被resue)
a.i Variants of LRU
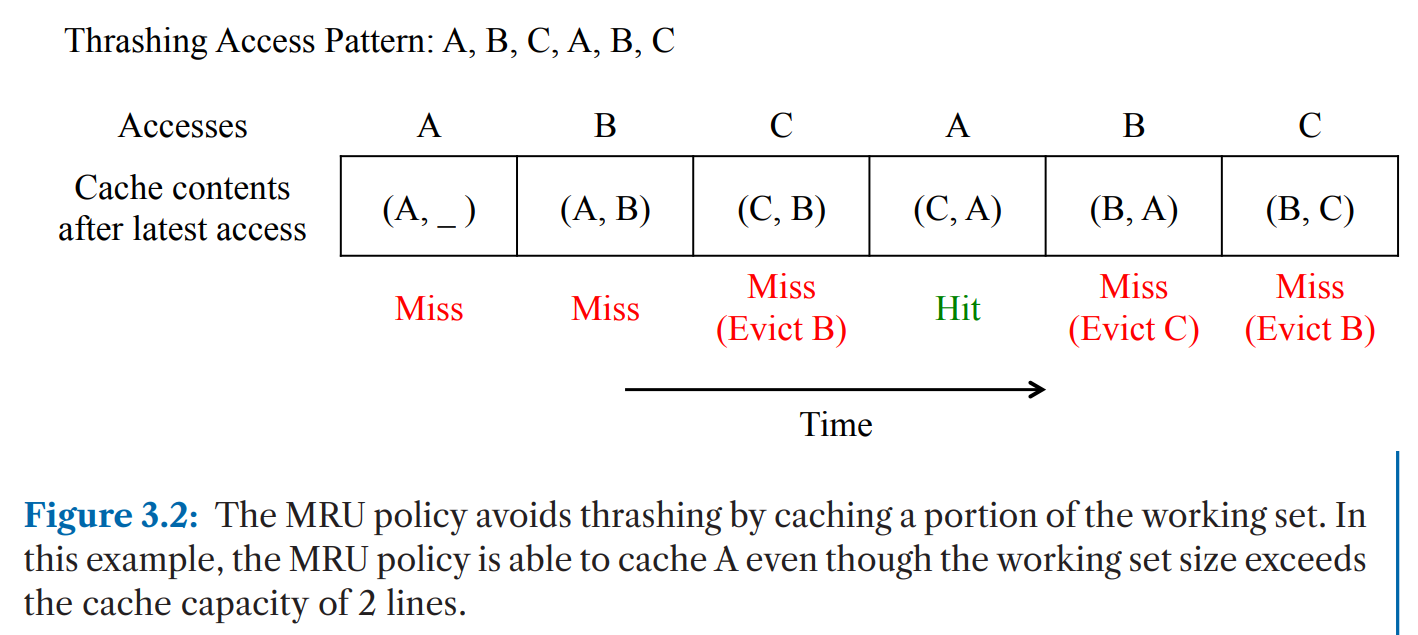
MRU
- good case
- thrashing
- bad case
- recency-friendly accesses
- 对working set变化不友好

Early Eviction LRU (EELRU)
Segmented LRU
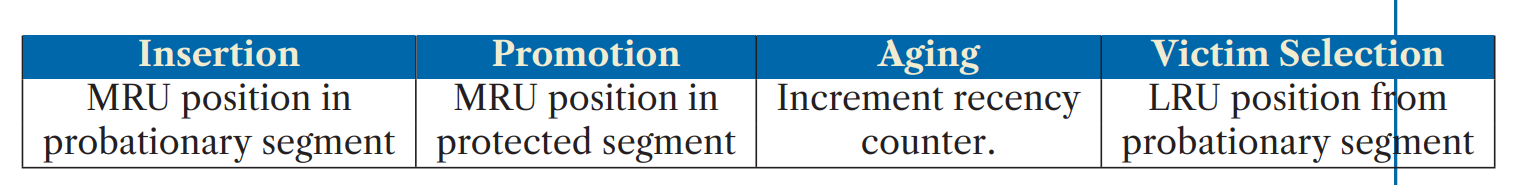
Segmented Least Recently Used (SLRU)是一个类似LRU的算法,结构上包含两个Segments
- a probational segment: 保存访问过一次的item
- a protected segment: 保存访问多余一次的item
在 SLRU 缓存中,如果那些被访问过多次的item比那些自插入以来没有被访问的键更有可能再次被访问,那么这种缓存会非常有效。(对scanning可以保持比较好的性能)
Lifecycle
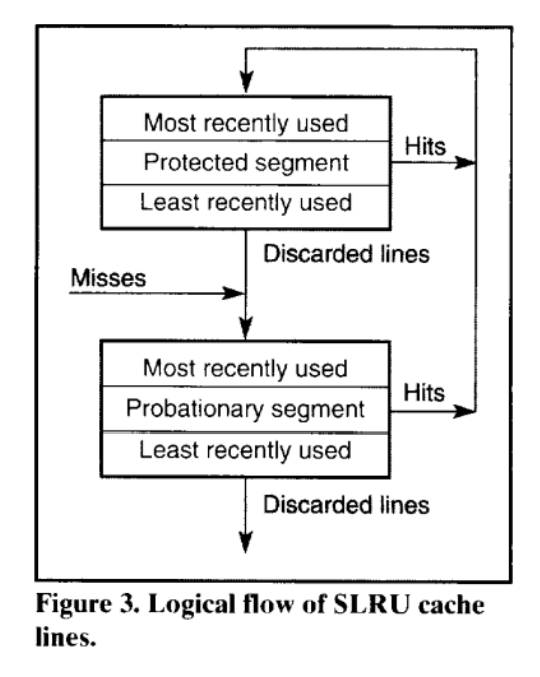
- New item is inserted to probational segment. This item becomes the most recently used item in the probational segment.
- If the probational segment is full, the least recently used item is evicted from cache.
- If an item in the probational segment is accessed (with get or set), the item is migrate to the protected segment. This item becomes the most recently used item of the protected segment.
- If the protected segment is full, the least recently used item from the segment is moved to probational segment. This item becomes the most recently used item in the probational segment. (从protected转移到probational)
- If an item in the protected segment is accessed, it becomes the most recently used item of the protected segment.
a.ii Beyond LRU: Insertion And Promotion Policies
Recency-Based policies可以通过修改insertion policy而不改变eviction policy来实现(保持evict LRU位置的cache line)
LRU insertion policy (LIP)
该策略将所有替换入Cache的行置于LRU端。相对于传统策略将所有替换入的行置于MRU端,LIP使一部分行得以驻留于Cache中,其驻留时间能比Cache本身容量更长。LIP策略能够很好地应对Thrashing,尤其对于循环访问内存的程序其性能近似于OPT策略。由于LIP中并没有引入Age,其无法响应Working Set的切换。

Bimodal Insertion Policy (BIP)
BIP策略是对LIP的加强和改进,新换入的行会小概率地被置于MRU端。BIP可以很好地响应Working Set的切换,并保持一定的命中率。
Dynamic Insertion Policy (DIP)
动态地在LRU和BIP间切换,选择其中命中率较高的策略执行后续指令。DIP对于LRU-friendly的程序块使用LRU策略,对于LRU-averse的程序块使用DIP策略,以求通用效率。对于1MB16路L2 Cache,DIP策略较LRU降低21%的失配率。
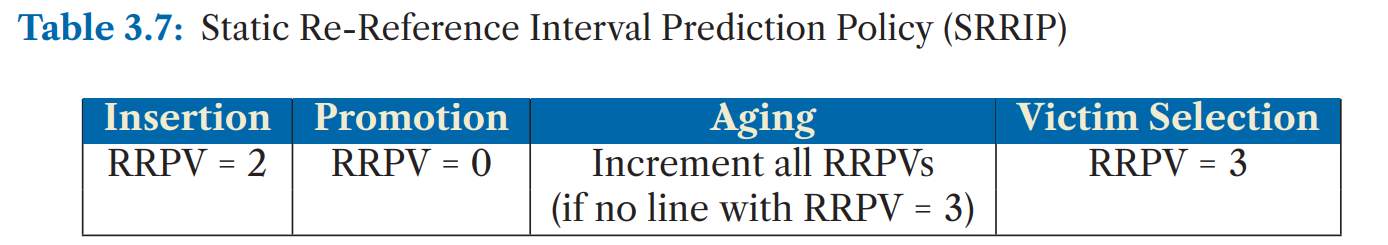
Re-Reference Interval Prediction (RRIP)
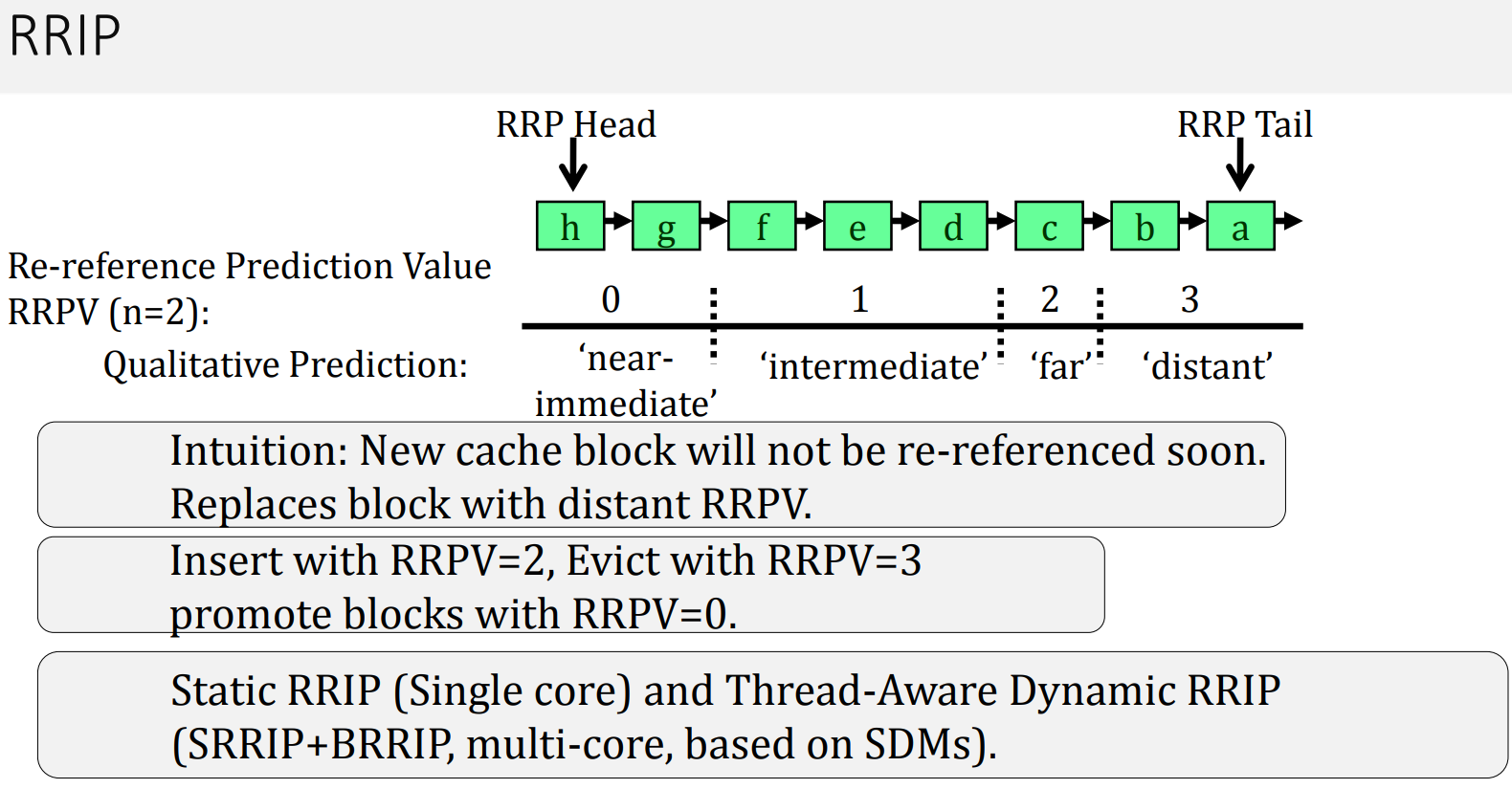
- SRRIP (Static)
每一个cache block附带一个M-bit的RRPV。
当一个cache hit,该cache block的RRPV bit被设置为“0”,表示在最近的将来,该cache block很有可能再被访问到;每当一个cache miss,替换算法会从左至右扫描RRPV bit为的block,如果找到则替换出该cache block,并将新插入的cache block 的RRPV bit置为 ,如果没有找到,那么将所有cache block的RRPV bit增加1,重新从左至右扫描。
上面将新插入的cache block设置为
- BRRIP (Bimodal)
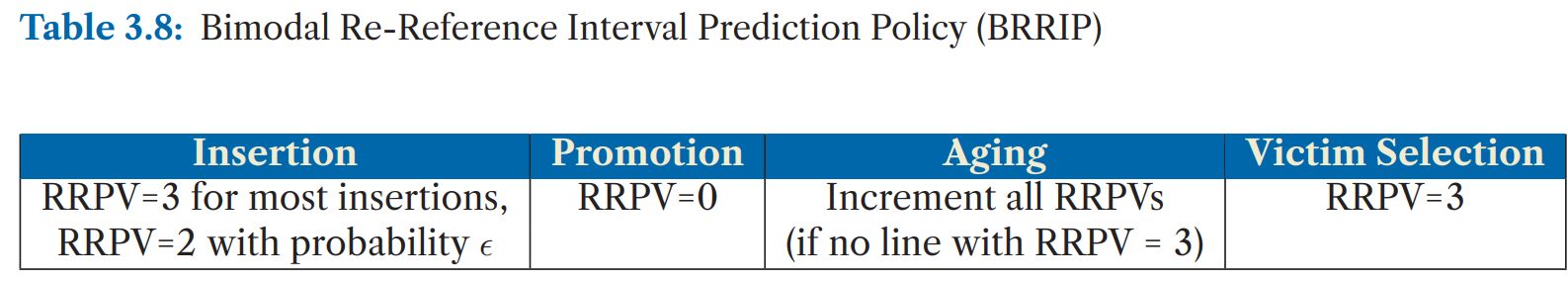
Protecting Distance-Based Policy (PDP)
Genetic Insertion and Promotion for PseudoLRU Replacement (GIPPR)
a.iii Extended Lifetime Recency-Based Policies
通过将一些cache line存储到auxiliary buffer或者victim cache来延长lifetime
The key motivation here is to defer eviction decisions to a later time when a more informed decision can be made.
Shepherd Cache
cache分为main和shepherd两部分,MC使用LRU,SC使用FIFO替换策略。
新的cacheline首先放入SC中,在此期间统计MC中的访问状况。若这个cacheline在离开SC时,MC中存在没有被访问的单元,则进行SC->MC的替换。但该方法的问题是lookahead来源于SC,但SC过大则会导致MC容量不足。
3.2 Frequency-based Policies
通过访问的frequency决定victim
a. Least Frequently Used (LFU)
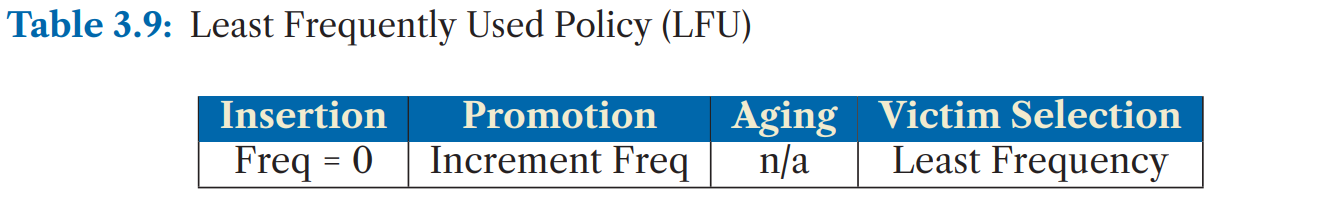
基本的LFU方法在每个cacheline上记录frequency counter, 在插入时初始化为0,每次访问增加计数,需要逐出时选择计数最小者。
但这样的问题是在发生应用phase变化时,旧的phase中的cacheline的计数都很高,无法完成替换。
b. Frequency-Based Replacement (FBR)
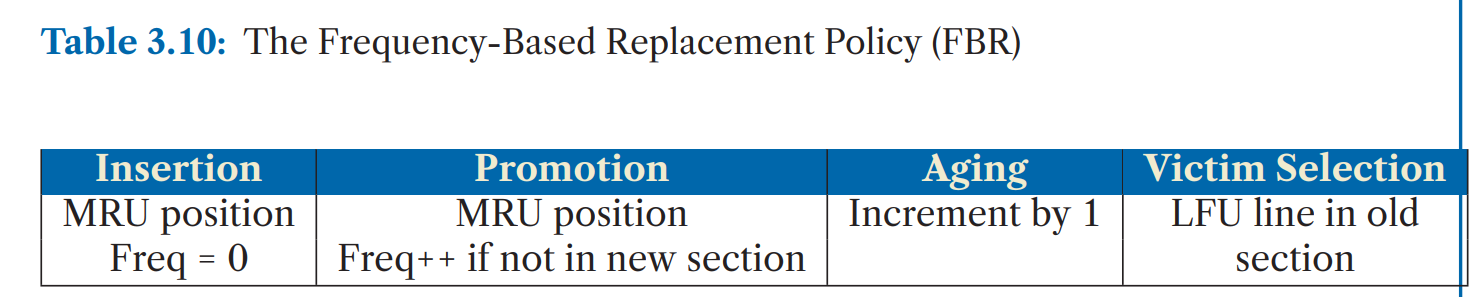
同时维护frequency和recency stack. 将recency stack分为new/middle/old三个区域,new区域的计数不增加,逐出old区域的LFU。
c. Least Recently/Frequently Used (LRFU)
联合利用recency和frequency信息,为每个cacheline计算Combined Recency and Frequency (CRF)信息
3.3 Hybrid Policies
核心思想:在不同workload/phase下灵活地选择替换策略。这有两个关键问题
- accurately identifying the policy that will be the most beneficial
- managing multiple policies at a low hardware cost
a. Adaptive Replacement Cache (ARC)
b. Set Dueling
在cache中选择一些用于“采样”的set, 低成本地实现不同policy效果的监控
a few randomly chosen sets can accurately represent the behavior of different replacement policies on the entire cache.
b.i Dynamic Insertion Policy (DIP)
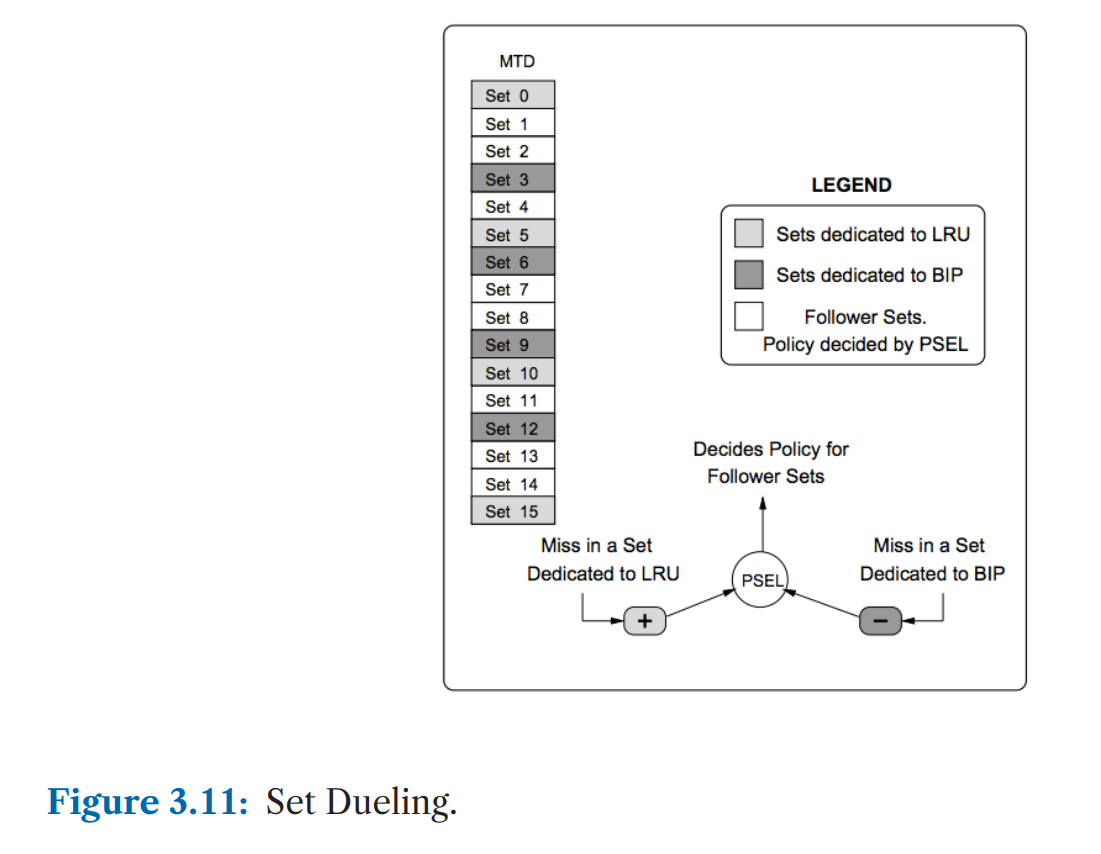
LRU和BIP的结合体
先选定一些做采样的set: Set Dueling Monitors (SDMs)。SDM中一些使用LRU,一些使用BIP。另外的set称为follewer sets。
如果SDM中LRU策略表现比较好(cache hit多),则follower sets就用LRU, 否则就用BIP
b.ii Dynamic Re-Reference Interval Policy (DRRIP)
SRRIP和BRRIP的结合体
4. Fine-Grained Replacement Policies
References
- 【读书笔记】《Cache Replacement Policies》 - 掘金
- GitHub - sjakthol/node-slru-cache: Segmented Least Recently Used Cache for Node.js
- https://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/biswap/CS422/L16-CR.pdf
- Cache Replacement Policies - winfred的文章 - 知乎 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/150664769